The estimation of cardiac output by the Nexfin device is of poor reliability for tracking the effects of a fluid challenge
- PMID: 23107227
- PMCID: PMC3682316
- DOI: 10.1186/cc11846
The estimation of cardiac output by the Nexfin device is of poor reliability for tracking the effects of a fluid challenge
Abstract
Introduction: The Nexfin device estimates arterial pressure by the volume clamp method through a finger pneumatic cuff. It also allows to estimate cardiac index (CInoninv) by pulse contour analysis of the non-invasive arterial pressure curve. We evaluated the ability of the device to track changes in cardiac index induced by a fluid challenge.
Methods: We included 45 patients for whom a volume expansion (500 mL of saline infused over 30 min) was planned. The volume expansion-induced changes in cardiac index measured by transpulmonary thermodilution (CIinv, PiCCO device) and in CInoninv were recorded.
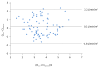
Results: In seven patients, the Nexfin could not record the arterial curve due to finger hypoperfusion. Considering both the values obtained before and after volume expansion (n = 76 pairs of measurements), the bias (lower and upper limits of agreement) between CIinv and CInoninv was 0.2 (-1.8 to 2.2) L/min/m2. The mean change in CInoninv was 10 ± 11%. The percentage error of CInoninv was 57%. The correlation between the changes in CIinv and CInoninv observed during volume expansion was significant (P = 0.0002) with an r2 = 0.31.
Conclusions: The estimation of CI by the Nexfin device in critically ill patients is not reliable, neither for estimating absolute values of CI nor for tracking its changes during volume expansion.
Figures


References
-
- Penaz J. Digest of the 10th International Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering. Dresden; 1973. Photoelectric measurement of blood pressure, volume and flow in the finger.
-
- Wesseling KH. In: Blood Pressure Measurement. Meyer-Sabellek W, Anlauf M, Gotzen R, Steinfeld L, editor. Darmstadt: Steinkopff Verlag; 1990. Finapres, continuous noninvasive finger arterial pressure based on the method of Pĕnáz; pp. 161–172.
-
- Hofhuizen CM, Lemson J, Hemelaar AE, Settels JJ, Schraa O, Singh SK, van der Hoeven JG, Scheffer GJ. Continuous non-invasive finger arterial pressure monitoring reflects intra-arterial pressure changes in children undergoing cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2010;16:493–500. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeq201. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

