Diagnostic and prognostic value of plasma and tissue ubiquitin-like, containing PHD and RING finger domains 1 in breast cancer patients
- PMID: 23107467
- PMCID: PMC7657185
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12052
Diagnostic and prognostic value of plasma and tissue ubiquitin-like, containing PHD and RING finger domains 1 in breast cancer patients
Abstract
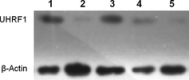
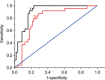
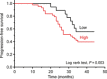
Ubiquitin-like, containing PHD and RING finger domains 1 (UHRF1) has been reported to play an important role in breast carcinogenesis. This work investigated the correlation of UHRF1 DNA level in plasma with clinical characteristics of breast cancer and its clinical significance in breast cancer diagnosis. The expression of UHRF1 in primary breast cancer tissue was examined by Western blot. The UHRF1 DNA levels in plasma and UHRF1 mRNA expression in tissues were determined by accurate real-time quantitative PCR. The associations of UHRF1 levels with clinical variables were evaluated using standard statistical methods. The UHRF1 DNA in plasma of 229 breast cancer patients showed higher expression than healthy controls, which showed high specificity up to 76.2% at a sensitivity of 79.2%, and was significantly associated with c-erbB2 positive status, cancer stage and lymph node metastasis. High UHRF1 DNA level in plasma was significantly associated with short progression-free survival. The UHRF1 DNA level in plasma is highly correlative with breast cancer and its status and stage, and may be a potential independent diagnostic and prognostic factor for both breast cancer and the survival of breast cancer patients.
© 2012 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of the UHRF1 expression in serum and tissue for gastric cancer detection.Biomarkers. 2015;20(3):183-8. doi: 10.3109/1354750X.2015.1061599. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Biomarkers. 2015. PMID: 26161699
-
Circ ubiquitin-like-containing plant homeodomain and RING finger domains protein 1 increases the stability of G9a and ubiquitin-like-containing plant homeodomain and RING finger domains protein 1 messenger RNA through recruiting eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A3, transcriptionally inhibiting PDZ and homeobox protein domain protein 1, and promotes the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Mar;39(3):596-607. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16408. Epub 2023 Dec 7. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38059880
-
Overexpression of UHRF1 is significantly associated with poor prognosis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Med Oncol. 2013 Dec;30(4):613. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0613-9. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Med Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24005809
-
[Role of UHRF1 in methylation regulation and angiogenesis].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Feb 10;37(2):200-204. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9406.2020.02.025. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32034755 Review. Chinese.
-
Role of UHRF1 in malignancy and its function as a therapeutic target for molecular docking towards the SRA domain.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019 Sep;114:105558. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2019.06.006. Epub 2019 Jun 22. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31238111 Review.
Cited by
-
Negative regulation of DNMT3A de novo DNA methylation by frequently overexpressed UHRF family proteins as a mechanism for widespread DNA hypomethylation in cancer.Cell Discov. 2016 Apr 12;2:16007. doi: 10.1038/celldisc.2016.7. eCollection 2016. Cell Discov. 2016. PMID: 27462454 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Analysis of the Maize PHD-Finger Gene Family Reveals a Subfamily Involved in Abiotic Stress Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Sep 30;16(10):23517-44. doi: 10.3390/ijms161023517. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26437398 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental and hormonal regulation of ubiquitin-like with plant homeodomain and really interesting new gene finger domains 1 gene expression in ovarian granulosa and theca cells of cattle.J Anim Sci. 2020 Jul 1;98(7):skaa205. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa205. J Anim Sci. 2020. PMID: 32614952 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insights into UHRF1‑mediated DNA methylation by structure‑based functional clarification of UHRF1 domains (Review).Oncol Lett. 2023 Nov 2;26(6):542. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.14129. eCollection 2023 Dec. Oncol Lett. 2023. PMID: 38020304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA Methylation Readers and Cancer: Mechanistic and Therapeutic Applications.Front Oncol. 2019 Jun 11;9:489. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00489. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31245293 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xu GW, Hu YS, Kan X. The preliminary report of breast cancer screening for 100000 women in China. China Cancer 2010; 19: 565–8.
-
- Weigelt B, Peterse JL, van't Veer LJ. Breast cancer metastasis: marker and models. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5: 591–602. - PubMed
-
- van't Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ et al Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 2002; 415: 530–6. - PubMed
-
- van de Vijver MJ, He YD, van't Veer LJ et al A gene‐expression signature as a predictor of survival in breast cancer. N Eng J Med 2002;347:1999–2009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

