A metabolic signature predicts biological age in mice
- PMID: 23107558
- PMCID: PMC3552107
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.12025
A metabolic signature predicts biological age in mice
Abstract
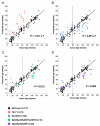
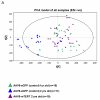
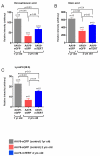
Our understanding of the mechanisms by which aging is produced is still very limited. Here, we have determined the sera metabolite profile of 117 wild-type mice of different genetic backgrounds ranging from 8 to 129 weeks of age. This has allowed us to define a robust metabolomic signature and a derived metabolomic score that reliably/accurately predicts the age of wild-type mice. In the case of telomerase-deficient mice, which have a shortened lifespan, their metabolomic score predicts older ages than expected. Conversely, in the case of mice that overexpress telomerase, their metabolic score corresponded to younger ages than expected. Importantly, telomerase reactivation late in life by using a TERT-based gene therapy recently described by us significantly reverted the metabolic profile of old mice to that of younger mice, further confirming an anti-aging role for telomerase. Thus, the metabolomic signature associated with natural mouse aging accurately predicts aging produced by telomere shortening, suggesting that natural mouse aging is in part produced by presence of short telomeres. These results indicate that the metabolomic signature is associated with the biological age rather than with the chronological age. This constitutes one of the first aging-associated metabolomic signatures in a mammalian organism.
© 2012 The Authors Aging Cell © 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd/Anatomical Society of Great Britain and Ireland.
Figures

References
-
- Allen J, Davey HM, Broadhurst D, Heald JK, Rowland JJ, Oliver SG, Kell DB. High-throughput classification of yeast mutants for functional genomics using metabolic footprinting. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21:692–696. - PubMed
-
- Barlow C, Hirotsune S, Paylor R, Liyanage M, Eckhaus M, Collins F, Shiloh Y, Crawley JN, Ried T, Tagle D, Wynshaw-Boris A. Atm-deficient mice: a paradigm of ataxia telangiectasia. Cell. 1996;86:159–171. - PubMed
-
- Barr J, Vazquez-Chantada M, Alonso C, Perez-Cormenzana M, Mayo R, Galan A, Caballeria J, Martin-Duce A, Tran A, Wagner C, Luka Z, Lu SC, Castro A, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Martinez-Chantar ML, Veyrie N, Clement K, Tordjman J, Gual P, Mato JM. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based parallel metabolic profiling of human and mouse model serum reveals putative biomarkers associated with the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Proteome Res. 2010;9:4501–4512. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blasco MA, Lee HW, Hande MP, Samper E, Lansdorp PM, DePinho RA, Greider CW. Telomere shortening and tumor formation by mouse cells lacking telomerase RNA. Cell. 1997;91:25–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

