Toll-like receptor 4 is required for α-synuclein dependent activation of microglia and astroglia
- PMID: 23108585
- PMCID: PMC3568908
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.22437
Toll-like receptor 4 is required for α-synuclein dependent activation of microglia and astroglia
Abstract
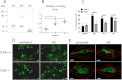
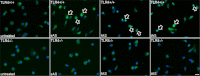
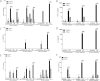
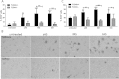
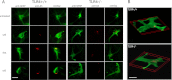
Alpha-synucleinopathies (ASP) are neurodegenerative disorders, characterized by accumulation of misfolded α-synuclein, selective neuronal loss, and extensive gliosis. It is accepted that microgliosis and astrogliosis contribute to the disease progression in ASP. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are expressed on cells of the innate immune system, including glia, and TLR4 dysregulation may play a role in ASP pathogenesis. In this study we aimed to define the involvement of TLR4 in microglial and astroglial activation induced by different forms of α-synuclein (full length soluble, fibrillized, and C-terminally truncated). Purified primary wild type (TLR4(+/+)) and TLR4 deficient (TLR4(-/-)) murine microglial and astroglial cell cultures were treated with recombinant α-synuclein and phagocytic activity, NFκB nuclear translocation, cytokine release, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production were measured. We show that TLR4 mediates α-synuclein-induced microglial phagocytic activity, pro-inflammatory cytokine release, and ROS production. TLR4(-/-) astroglia present a suppressed pro-inflammatory response and decreased ROS production triggered by α-synuclein treatment. However, the uptake of α-synuclein by primary astroglia is not dependent on TLR4 expression. Our results indicate the C-terminally truncated form as the most potent inductor of TLR4-dependent glial activation. The current findings suggest that TLR4 plays a modulatory role on glial pro-inflammatory responses and ROS production triggered by α-synuclein. In contrast to microglia, the uptake of alpha-synuclein by astroglia is not dependent on TLR4. Our data provide novel insights into the mechanisms of α-synuclein-induced microglial and astroglial activation which may have an impact on understanding the pathogenesis of ASP.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Akira S. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Adv Immunol. 2001;78:1–56. - PubMed
-
- Al-Chalabi A, Durr A, Wood NW, Parkinson MH, Camuzat A, Hulot JS, Morrison KE, Renton A, Sussmuth SD, Landwehrmeyer BG, Ludolph A, Agid Y, Brice A, Leigh PN, Bensimon G. Genetic variants of the alpha-synuclein gene SNCA are associated with multiple system atrophy. PLoS One. 2009;4:e7114. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Erviti L, Couch Y, Richardson J, Cooper JM, Wood MJ. Alpha-synuclein release by neurons activates the inflammatory response in a microglial cell line. Neurosci Res. 2011;69:337–342. - PubMed
-
- Apetri MM, Maiti NC, Zagorski MG, Carey PR, Anderson VE. Secondary structure of alpha-synuclein oligomers: Characterization by raman and atomic force microscopy. J Mol Biol. 2006;355:63–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

