Molecular mechanisms of N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-induced superoxide generation and degranulation in mouse neutrophils: phospholipase D is dispensable
- PMID: 23109426
- PMCID: PMC3536298
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00869-12
Molecular mechanisms of N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-induced superoxide generation and degranulation in mouse neutrophils: phospholipase D is dispensable
Abstract
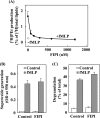
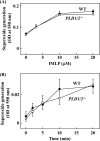
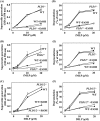
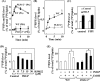
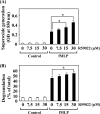
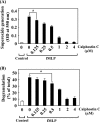
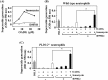
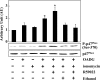
Phospholipase D (PLD), which produces the lipid messenger phosphatidic acid (PA), has been implicated in superoxide generation and degranulation in neutrophils. The basis for this conclusion is the observation that primary alcohols, which interfere with PLD-catalyzed PA production, inhibit these neutrophil functions. However, off-target effects of primary alcohols cannot be totally excluded. Here, we generated PLD(-/-) mice in order to reevaluate the involvement of PLD in and investigate the molecular mechanisms of these neutrophil functions. Surprisingly, N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP) induced these functions in PLD(-/-) neutrophils, and these functions were suppressed by ethanol. These results indicate that PLD is dispensable for these neutrophil functions and that ethanol nonspecifically inhibits them, warning against the use of primary alcohols as specific inhibitors of PLD-mediated PA formation. The calcium ionophore ionomycin and the membrane-permeative compound 1-oleoyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol (OADG) synergistically induced superoxide generation. On the other hand, ionomycin alone induced degranulation, which was further augmented by OADG. These results demonstrate that conventional protein kinase C (cPKC) is crucial for superoxide generation, and a Ca(2+)-dependent signaling pathway(s) and cPKC are involved in degranulation in mouse neutrophils.
Figures




References
-
- Smith JA. 1994. Neutrophils, host defense, and inflammation: a double-edged sword. J. Leukoc. Biol. 56: 672–686 - PubMed
-
- Nordenfelt P, Tapper H. 2011. Phagosome dynamics during phagocytosis by neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 90: 271–284 - PubMed
-
- Iiri T, Tohkin M, Morishima N, Ohoka Y, Ui M, Katada T. 1989. Chemotactic peptide receptor-supported ADP-ribosylation of a pertussis toxin substrate GTP-binding protein by cholera toxin in neutrophil-type HL-60 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 264: 21394–21400 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
