Initial molecular response at 3 months may predict both response and event-free survival at 24 months in imatinib-resistant or -intolerant patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase treated with nilotinib
- PMID: 23109697
- PMCID: PMC4979159
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2011.40.5217
Initial molecular response at 3 months may predict both response and event-free survival at 24 months in imatinib-resistant or -intolerant patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase treated with nilotinib
Abstract
Purpose: The association between initial molecular response and longer-term outcomes with nilotinib was examined.
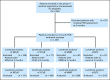
Patients and methods: Patients with imatinib-resistant or -intolerant chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase from the phase II nilotinib registration study with available postbaseline BCR-ABL1 transcript assessments were included (N = 237).
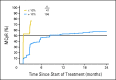
Results: BCR-ABL1 transcript levels (International Scale [IS]) at 3 months correlated with complete cytogenetic response (CCyR) by 24 months. Patients with BCR-ABL1 (IS) of > 1% to ≤ 10% at 3 months with nilotinib had higher cumulative incidence of CCyR by 24 months than patients with BCR-ABL1 (IS) of > 10% (53% v 16%). BCR-ABL1 (IS) at 3 months predicted major molecular response (MMR) by 24 months. Cumulative incidence of MMR by 24 months for patients with BCR-ABL1 (IS) of > 0.1% to ≤ 1%, > 1% to ≤ 10%, and > 10% was 65%, 27%, and 9%, respectively. These differences were observed for patients with or without baseline BCR-ABL1 mutations and for those with imatinib resistance or intolerance. Estimated event-free survival (EFS) rates at 24 months decreased with higher transcript levels at 3 months; patients with BCR-ABL1 (IS) of ≤ 1% had an estimated 24-month EFS rate of 82%, compared with 70% for patients with BCR-ABL1 (IS) of > 1% to ≤ 10% and 48% for patients with BCR-ABL1 (IS) of > 10%.
Conclusion: Patients with BCR-ABL1 (IS) of > 10% at 3 months had a lower cumulative incidence of CCyR and MMR and lower rates of EFS versus patients with BCR-ABL1 (IS) of ≤ 10%. Prospective studies may determine whether close monitoring or alternative therapies are warranted for patients with minimal initial molecular response.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00471497.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Weisberg E, Manley PW, Breitenstein W, et al. Characterization of AMN107, a selective inhibitor of native and mutant Bcr-Abl. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:129–141. - PubMed
-
- Golemovic M, Verstovsek S, Giles F, et al. AMN107, a novel aminopyrimidine inhibitor of Bcr-Abl, has in vitro activity against imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:4941–4947. - PubMed
-
- Manley PW, Drueckes P, Fendrich G, et al. Extended kinase profile and properties of the protein kinase inhibitor nilotinib. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1804:445–453. - PubMed
-
- Kantarjian HM, Giles F, Gattermann N, et al. Nilotinib (formerly AMN107), a highly selective BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is effective in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase following imatinib resistance and intolerance. Blood. 2007;110:3540–3546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

