Is DNA damage response ready for action anywhere?
- PMID: 23109871
- PMCID: PMC3472763
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms130911569
Is DNA damage response ready for action anywhere?
Abstract
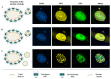
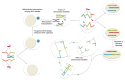
Organisms are continuously exposed to DNA damaging agents, consequently, cells have developed an intricate system known as the DNA damage response (DDR) in order to detect and repair DNA lesions. This response has to be rapid and accurate in order to keep genome integrity. It has been observed that the condensation state of chromatin hinders a proper DDR. However, the condensation state of chromatin is not the only barrier to DDR. In this review, we have collected data regarding the presence of DDR factors on micronuclear DNA lesions that indicate that micronuclei are almost incapable of generating an effective DDR because of defects in their nuclear envelope. Finally, considering the recent observations about the reincorporation of micronuclei to the main bulk of chromosomes, we suggest that, under certain circumstances, micronuclei carrying DNA damage might be a source of chromosome instability.
Keywords: DSB repair; NER pathway; chromosome instability; micronuclei.
Figures
References
-
- Fenech M., Kirsch-Volders M., Natarajan A.T., Surralles J., Crott J.W., Parry J., Norppa H., Eastmond D.A., Tucker J.D., Thomas P. Molecular Mechanisms of Micronucleus, Nucleoplasmic Bridge and Nuclear Bud Formation in Mammalian and Human Cells. Mutagenesis. 2011;26:125–132. - PubMed
-
- Shay J.W., Wright W.E. Senescence and Immortalization: Role of Telomeres and Telomerase. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26:867–874. - PubMed
-
- Latre L., Tusell L., Martin M., Miro R., Egozcue J., Blasco M.A., Genesca A. Shortened Telomeres Join to DNA Breaks Interfering with their Correct Repair. Exp. Cell Res. 2003;287:282–288. - PubMed
-
- Hoffelder D.R., Luo L., Burke N.A., Watkins S.C., Gollin S.M., Saunders W.S. Resolution of Anaphase Bridges in Cancer Cells. Chromosoma. 2004;112:389–397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

