Genetic activation of BK currents in vivo generates bidirectional effects on neuronal excitability
- PMID: 23112153
- PMCID: PMC3503162
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1205573109
Genetic activation of BK currents in vivo generates bidirectional effects on neuronal excitability
Abstract
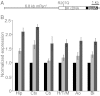
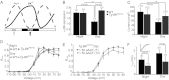
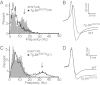
Large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels (BK) are potent negative regulators of excitability in neurons and muscle, and increasing BK current is a novel therapeutic strategy for neuro- and cardioprotection, disorders of smooth muscle hyperactivity, and several psychiatric diseases. However, in some neurons, enhanced BK current is linked with seizures and paradoxical increases in excitability, potentially complicating the clinical use of agonists. The mechanisms that switch BK influence from inhibitory to excitatory are not well defined. Here we investigate this dichotomy using a gain-of-function subunit (BK(R207Q)) to enhance BK currents. Heterologous expression of BK(R207Q) generated currents that activated at physiologically relevant voltages in lower intracellular Ca(2+), activated faster, and deactivated slower than wild-type currents. We then used BK(R207Q) expression to broadly augment endogenous BK currents in vivo, generating a transgenic mouse from a circadian clock-controlled Period1 gene fragment (Tg-BK(R207Q)). The specific impact on excitability was assessed in neurons of the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in the hypothalamus, a cell type where BK currents regulate spontaneous firing under distinct day and night conditions that are defined by different complements of ionic currents. In the SCN, Tg-BK(R207Q) expression converted the endogenous BK current to fast-activating, while maintaining similar current-voltage properties between day and night. Alteration of BK currents in Tg-BK(R207Q) SCN neurons increased firing at night but decreased firing during the day, demonstrating that BK currents generate bidirectional effects on neuronal firing under distinct conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hille B. Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes. 3rd Ed. MA: Sinauer, Sunderland; 2001. p. xviii, 814.
-
- Meredith AL, Thorneloe KS, Werner ME, Nelson MT, Aldrich RW. Overactive bladder and incontinence in the absence of the BK large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(35):36746–36752. - PubMed
-
- Butler A, Tsunoda S, McCobb DP, Wei A, Salkoff L. mSlo, a complex mouse gene encoding “maxi” calcium-activated potassium channels. Science. 1993;261(5118):221–224. - PubMed
-
- Tseng-Crank J, et al. Cloning, expression, and distribution of functionally distinct Ca(2+)-activated K+ channel isoforms from human brain. Neuron. 1994;13(6):1315–1330. - PubMed
-
- Salkoff L, Butler A, Ferreira G, Santi C, Wei A. High-conductance potassium channels of the SLO family. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7(12):921–931. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

