Transcriptome-wide analyses of CstF64-RNA interactions in global regulation of mRNA alternative polyadenylation
- PMID: 23112178
- PMCID: PMC3503179
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1211101109
Transcriptome-wide analyses of CstF64-RNA interactions in global regulation of mRNA alternative polyadenylation
Abstract
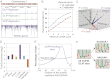
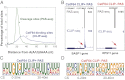
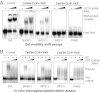
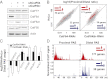
Cleavage stimulation factor 64 kDa (CstF64) is an essential pre-mRNA 3' processing factor and an important regulator of alternative polyadenylation (APA). Here we characterized CstF64-RNA interactions in vivo at the transcriptome level and investigated the role of CstF64 in global APA regulation through individual nucleotide resolution UV crosslinking and immunoprecipitation sequencing and direct RNA sequencing analyses. We observed highly specific CstF64-RNA interactions at poly(A) sites (PASs), and we provide evidence that such interactions are widely variable in affinity and may be differentially required for PAS recognition. Depletion of CstF64 by RNAi has a relatively small effect on the global APA profile, but codepletion of the CstF64 paralog CstF64τ leads to greater APA changes, most of which are characterized by the increased relative use of distal PASs. Finally, we found that CstF64 binds to thousands of dormant intronic PASs that are suppressed, at least in part, by U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. Taken together, our findings provide insight into the mechanisms of PAS recognition and identify CstF64 as an important global regulator of APA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overlapping and distinct functions of CstF64 and CstF64τ in mammalian mRNA 3' processing.RNA. 2013 Dec;19(12):1781-90. doi: 10.1261/rna.042317.113. Epub 2013 Oct 22. RNA. 2013. PMID: 24149845 Free PMC article.
-
A potential mechanism underlying U1 snRNP inhibition of the cleavage step of mRNA 3' processing.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Sep 10;530(1):196-202. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.06.092. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32828285
-
The U1 antisense morpholino oligonucleotide (AMO) disrupts U1 snRNP structure to promote intronic PCPA modification of pre-mRNAs.J Biol Chem. 2023 Jul;299(7):104854. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104854. Epub 2023 May 22. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37224962 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding proteins in regulation of alternative cleavage and polyadenylation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;825:97-127. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1221-6_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 25201104 Review.
-
Integrating transcription kinetics with alternative polyadenylation and cell cycle control.Nucleus. 2011 Nov-Dec;2(6):556-61. doi: 10.4161/nucl.2.6.18064. Epub 2011 Nov 1. Nucleus. 2011. PMID: 22127258 Review.
Cited by
-
αCP Poly(C) binding proteins act as global regulators of alternative polyadenylation.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jul;33(13):2560-73. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01380-12. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23629627 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling between alternative polyadenylation and alternative splicing is limited to terminal introns.RNA Biol. 2016 Jul 2;13(7):646-55. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1191727. Epub 2016 May 31. RNA Biol. 2016. PMID: 27245359 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of Gle1 impacts DDX1 at transcription termination sites.Mol Biol Cell. 2020 Oct 1;31(21):2398-2408. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-03-0215. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Mol Biol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32755435 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative polyadenylation of mRNA and its role in cancer.Genes Dis. 2019 Oct 25;8(1):61-72. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2019.10.011. eCollection 2021 Jan. Genes Dis. 2019. PMID: 33569514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CSTF2-impeded innate αβ T cell infiltration and activation exacerbate immune evasion of pancreatic cancer.Cell Death Differ. 2025 May;32(5):973-988. doi: 10.1038/s41418-025-01464-0. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Cell Death Differ. 2025. PMID: 39972059
References
-
- Colgan DF, Manley JL. Mechanism and regulation of mRNA polyadenylation. Genes Dev. 1997;11(21):2755–2766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

