Neutrophils orchestrate their own recruitment in murine arthritis through C5aR and FcγR signaling
- PMID: 23112187
- PMCID: PMC3503206
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1213797109
Neutrophils orchestrate their own recruitment in murine arthritis through C5aR and FcγR signaling
Abstract
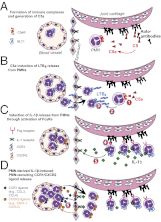
Neutrophil recruitment into the joint is a hallmark of inflammatory arthritides, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In a mouse model of autoantibody-induced inflammatory arthritis, neutrophils infiltrate the joint via multiple chemoattractant receptors, including the leukotriene B(4) (LTB(4)) receptor BLT1 and the chemokine receptors CCR1 and CXCR2. Once in the joint, neutrophils perpetuate their own recruitment by releasing LTB(4) and IL-1β, presumably after activation by immune complexes deposited on joint structures. Two pathways by which immune complexes may activate neutrophils include complement fixation, resulting in the generation of C5a, and direct engagement of Fcγ receptors (FcγRs). Previous investigations showed that this model of autoantibody-induced arthritis requires the C5a receptor C5aR and FcγRs, but the simultaneous necessity for both pathways was not understood. Here we show that C5aR and FcγRs work in sequence to initiate and sustain neutrophil recruitment in vivo. Specifically, C5aR activation of neutrophils is required for LTB(4) release and early neutrophil recruitment into the joint, whereas FcγR engagement upon neutrophils induces IL-1β release and subsequent neutrophil-active chemokine production, ensuring continued inflammation. These findings support the concept that immune complex-mediated leukocyte activation is not composed of overlapping and redundant pathways, but that each element serves a distinct and critical function in vivo, culminating in tissue inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

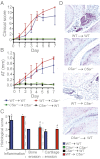
 Alox5−/−” and “C5ar−/− PMNs
Alox5−/−” and “C5ar−/− PMNs  Alox5−/−”) together with K/BxN serum i.v. on days 0 and 2. Alox5−/− mice receiving only K/BxN serum served as controls. Mice were clinically scored daily (n = 4–5 mice per group; one representative of three independent experiments is shown). P < 0.001 for WT PMNs
Alox5−/−”) together with K/BxN serum i.v. on days 0 and 2. Alox5−/− mice receiving only K/BxN serum served as controls. Mice were clinically scored daily (n = 4–5 mice per group; one representative of three independent experiments is shown). P < 0.001 for WT PMNs  Alox5−/− vs. C5ar−/− PMNs
Alox5−/− vs. C5ar−/− PMNs  Alox5−/− or Alox5−/− controls in clinical score and ankle thickening. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
Alox5−/− or Alox5−/− controls in clinical score and ankle thickening. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.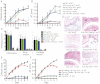
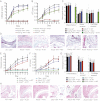
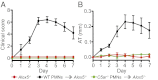
 Il1a−/−Il1b−/− → WT; Fcer1g−/− PMNs
Il1a−/−Il1b−/− → WT; Fcer1g−/− PMNs  Il1a−/−Il1b−/− → WT) with K/BxN serum on days 0 and 2. WT → WT and Il1a−/−Il1b−/− → WT chimera obtaining only K/BxN serum served as controls (n = 4 mice per group; one representative of three independent experiments is shown). P < 0.001 for WT PMNs
Il1a−/−Il1b−/− → WT) with K/BxN serum on days 0 and 2. WT → WT and Il1a−/−Il1b−/− → WT chimera obtaining only K/BxN serum served as controls (n = 4 mice per group; one representative of three independent experiments is shown). P < 0.001 for WT PMNs  Il1a−/−Il1b−/− → WT vs. Fcer1g−/− PMNs
Il1a−/−Il1b−/− → WT vs. Fcer1g−/− PMNs  Il1a−/−Il1b−/− → WT or vs. Il1a−/−Il1b−/− → WT chimera in clinical score and AT. All data presented are mean ± SEM.
Il1a−/−Il1b−/− → WT or vs. Il1a−/−Il1b−/− → WT chimera in clinical score and AT. All data presented are mean ± SEM.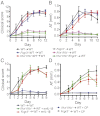
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

