Simultaneous targeting of COX-2 and AKT using selenocoxib-1-GSH to inhibit melanoma
- PMID: 23112250
- PMCID: PMC3546139
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0492
Simultaneous targeting of COX-2 and AKT using selenocoxib-1-GSH to inhibit melanoma
Abstract
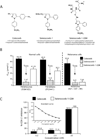
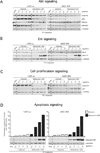
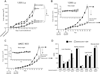
Melanoma is a highly metastatic and deadly disease. An agent simultaneously targeting the COX-2, PI3K/Akt, and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways that are deregulated in up to 70% of sporadic melanomas might be an effective treatment, but no agent of this type exists. To develop a single drug inhibiting COX-2 and PI3K/Akt signaling (and increasing MAPK pathway activity to inhibitory levels as a result of Akt inhibition), a selenium-containing glutathione (GSH) analogue of celecoxib, called selenocoxib-1-GSH was synthesized. It killed melanoma cells with an average IC(50) of 7.66 μmol/L compared with control celecoxib at 55.6 μmol/L. The IC(50) range for normal cells was 36.3 to 41.2 μmol/L compared with 7.66 μmol/L for cancer cells. Selenocoxib-1-GSH reduced development of xenografted tumor by approximately 70% with negligible toxicity by targeting COX-2, like celecoxib, and having novel inhibitory properties by acting as a PI3K/Akt inhibitor (and MAPK pathway activator to inhibitory levels due to Akt inhibition). The consequence of this inhibitory activity was an approximately 80% decrease in cultured cell proliferation and an approximately 200% increase in apoptosis following 24-hour treatment with 15.5 μmol/L of drug. Thus, this study details the development of selenocoxib-1-GSH, which is a nontoxic agent that targets the COX-2 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways in melanomas to inhibit tumor development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synergistic inhibitory effects of Celecoxib and Plumbagin on melanoma tumor growth.Cancer Lett. 2017 Jan 28;385:243-250. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.10.016. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 27769779 Free PMC article.
-
PBISe, a novel selenium-containing drug for the treatment of malignant melanoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 May;7(5):1297-308. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-2267. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18483317
-
Synthesis and antitumor properties of selenocoxib-1 against rat prostate adenocarcinoma cells.Int J Cancer. 2010 Jul 1;127(1):230-8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25033. Int J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 19918950
-
The Akt signaling pathway: an emerging therapeutic target in malignant melanoma.Cancer Biol Ther. 2011 Dec 15;12(12):1032-49. doi: 10.4161/cbt.12.12.18442. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011. PMID: 22157148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-Content Screening Pipeline for Natural Products Targeting Oncogenic Signaling in Melanoma.J Nat Prod. 2022 Apr 22;85(4):1006-1017. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.1c01154. Epub 2022 Mar 1. J Nat Prod. 2022. PMID: 35231173 Review.
Cited by
-
First Generation of Antioxidant Precursors for Bioisosteric Se-NSAIDs: Design, Synthesis, and In Vitro and In Vivo Anticancer Evaluation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Aug 24;12(9):1666. doi: 10.3390/antiox12091666. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37759969 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the structure-activity relationship of leelamine necessary for inhibiting intracellular cholesterol transport.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 25;8(17):28260-28277. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16002. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423677 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Heteroaryl Selenocyanates and Diselenides as Potent Antileishmanial Agents.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 May 23;60(6):3802-12. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02529-15. Print 2016 Jun. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27067328 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic inhibitory effects of Celecoxib and Plumbagin on melanoma tumor growth.Cancer Lett. 2017 Jan 28;385:243-250. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.10.016. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 27769779 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-targeted approach to suppress tumor-promoting inflammation.Semin Cancer Biol. 2015 Dec;35 Suppl:S151-S184. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 May 5. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015. PMID: 25951989 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Oliveria SA, Hay JL, Geller AC, Heneghan MK, McCabe MS, Halpern AC. Melanoma survivorship: research opportunities. J Cancer Surviv. 2007;1:87–97. - PubMed
-
- Wolchok JD, Neyns B, Linette G, Negrier S, Lutzky J, Thomas L, et al. Ipilimumab monotherapy in patients with pretreated advanced melanoma: a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 2, dose-ranging study. Lancet Oncol. 11:155–164. - PubMed
-
- Smalley KS, Sondak VK. Melanoma--an unlikely poster child for personalized cancer therapy. N Engl J Med. 363:876–878. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

