Febuxostat: a novel agent for management of hyperuricemia in gout
- PMID: 23112391
- PMCID: PMC3480742
- DOI: 10.4103/0250-474X.100231
Febuxostat: a novel agent for management of hyperuricemia in gout
Abstract
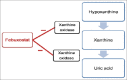
Gout is a metabolic disorder characterized by elevated uric acid levels in the body, associated with painful arthritis, tophi and nephropathy. The most frequently used pharmacologic urate lowering strategies involve reducing urate production with a xanthine oxidase inhibitor and enhancing urinary excretion of uric acid with a uricosuric agent. Urate lowering agents are limited in number, availability and effectiveness. The emergence of a new medication, febuxostat, to lower serum urate levels is welcome as no new drug have been approved since the introduction of allopurinol, in 1964, and the drugs that are available have limitations owing to inefficacy or toxicity. Febuxostat is a novel, nonpurine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, is a potential alternative to allopurinol for patients with hyperuricemia and gout.
Keywords: Gout; hyperuricemia; xanthine oxidase inhibitor.
References
-
- Roubenoff R, Klag MJ, Mead LA, Liang KY, Seidler AJ, Hochberg MC. Incidence and risk factors for gout in white men. JAMA. 1991;266:3004–7. - PubMed
-
- Kramer HM, Curhan G. The association between gout and nephrolithiasis: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III, 1988-1994. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;40:37–42. - PubMed
-
- Wallace KL, Riedel AA, Joseph-Ridge N, Wortmann R. Increasing prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia over 10 years among older adults in a managed care population. J Rheumatol. 2004;31:1582–7. - PubMed
-
- Becker MA, Jolly M. Metabolic bone and joint disease. In: Koopman WJ, Moreland LW, editors. Arthritis and allied conditions: A textbook of rheumatology. 15th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2005. pp. 2303–39.
-
- Terkeltaub RA. Gout. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1647–55. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources