Synthesis and Evaluation of N-substituted Imidazole Derivatives for Antimicrobial Activity
- PMID: 23112404
- PMCID: PMC3480755
- DOI: 10.4103/0250-474X.100246
Synthesis and Evaluation of N-substituted Imidazole Derivatives for Antimicrobial Activity
Abstract
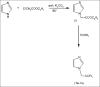
A series of N-substituted imidazole derivatives was synthesized. Imidazole nucleus was reacted with ethylchloroacetate to form imidazole ester. Reaction of the imidazole ester (I) with different amines yields the desired products (1a- 1e). The compounds were characterized by FT-IR, (1)H-NMR and mass spectra. The synthesized compounds were evaluated for the antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Candida albicans and Aspergillus niger by determination of MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) using tube dilution method. Compound (1b) was found to be the most active antimicrobial compound amongst others in the series.
Keywords: 1H-NMR; FT-IR; imidazole; minimum inhibitory concentration; tube dilution method.
Figures
References
-
- Rice LB. Unmet medical needs in antibacterial therapy. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;71:991–5. - PubMed
-
- Song JH. What's new on the antimicrobial horizon? Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2008;32(Suppl4):S207–13. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Zhang P, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Li Y, Wang Y. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a novel series of 1,5-benzothiazepine derivatives as potential antimicrobial agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2009;44:2815–21. - PubMed
-
- Zhang P, Wang LZ, Wu HS, Lan JM, Li Y, Wang YX. The synthesis and biological evaluation of a series of novel 2-COOC2H5/COONa substituted 1,5-benzothiazepine derivatives as antimicrobial agents. Chin Chem Lett. 2009;20:660–2.
-
- Sztanke K, Tuzimski T, Rzymowska J, Pasternak K, Kandefer-Szerszen M. Synthesis, determination of the lipophilicity, anticancer and antimicrobial properties of some fused 1,2,4-triazole derivatives. Eur J Med Chem. 2008;43:404–19. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources