Evaluation and treatment of surgical management of silicone mastitis
- PMID: 23112516
- PMCID: PMC3483577
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-2077.101380
Evaluation and treatment of surgical management of silicone mastitis
Abstract
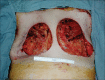
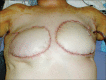
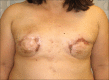
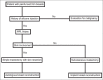
Injected liquid silicone continues to be employed by unscrupulous practitioners in many parts of the world for the purpose of breast augmentation. Complications vary; however, inflammation, foreign body reaction, and granuloma formation often lead to painful and disfigured breasts. Furthermore, migrations of silicone to remote tissues cause additional problems. We present a review of cases and propose an updated algorithm for the diagnosis and management silicone mastitis. We describe two representative cases of mastitis cause by injected liquid silicone. Patients uniformly developed inflammation and granuloma formation causing painful and disfigured breasts. Each patient required bilateral mastectomy and breast reconstruction. Although injection of liquid silicone has been condemned by the legitimate medical community for the purpose of breast augmentation, it continues to be illicitly performed and there exists a sizable patient population suffering from the complications of this procedure. Accurate identification requires a high index of suspicion in patients presenting with firm and painful breasts. An aggressive management strategy is recommended in the setting of silicone mastitis due to the risk of obscuring malignancy.
Keywords: Foreign body; granuloma; mastitis; silicone.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Wustrack KO, Zarem HA. Surgical management of silicone mastitis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1979;63:224–9. - PubMed
-
- Chen TH. Silicone injection granulomas of the breast: Treatment by subcutaneous mastectomy and immediate subpectoral breast implant. Br J Plast Surg. 1995;48:71–6. - PubMed
-
- Ortiz-Monasterio F, Trigos I. Management of patients with complications from injections of foreign materials into the breasts. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1972;50:42–7. - PubMed

