Optimization of pellets containing solid dispersion prepared by extrusion/spheronization using central composite design and desirability function
- PMID: 23112533
- PMCID: PMC3483524
- DOI: 10.4103/0975-1483.100020
Optimization of pellets containing solid dispersion prepared by extrusion/spheronization using central composite design and desirability function
Abstract
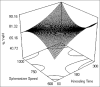
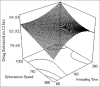
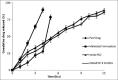
Furosemide is a class IV biopharmaceutical classification system drug having poor water solubility and low bioavailability due to the hepatic first-pass metabolism and has a short half-life of 2 h. To overcome the above drawback, this study was carried to prepare and evaluate the pellets containing furosemide solid dispersion (SD) for oral administration prepared by extrusion/spheronization. SD of furosemide was prepared with Eudragit L-100 at a drug-to-polymer ratio of 1:2 by employing a solvent evaporation method and characterized. Further, microcrystalline cellulose pellets containing SD were consequently prepared using a lab scale extrusion/ spheronizer and evaluated for in vitro drug release studies. The influence of process parameters used during extrusion/spheronization on the pellet properties was also studied using 2-factor, 3-level central composite design in order to improve the product quality. Additionally, the desirability function approach was applied to acquire the preeminent compromise between the multiple responses. Pellets containing solid dispersion (PSD) were prepared using optimal parameter settings demonstrated 88.52 ± 0.69% of the drug was released in a sustained release manner till 12 h. In vitro drug release data were fitted to various release kinetics models to study the mechanism of drug release. Drug release from the PSD was found to follow zero-order and Higuchi's model. Both studied parameters had great influence on the responses. PSD showed augmentation in the drug release profile till 12 h. The final optimized formulation was obtained by encapsulating best SD formulation within the pellet core to release the drug in the most soluble form in stomach and a sustained fashion in intestine.
Keywords: Central composite design; desirability function; furosemide; solid dispersion; sustained release pellets.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Response surface methodology and process optimization of sustained release pellets using Taguchi orthogonal array design and central composite design.J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2012 Jan;3(1):30-40. doi: 10.4103/2231-4040.93565. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2012. PMID: 22470891 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation and evaluation of sustained release enteric-coated pellets of budesonide for intestinal delivery.Int J Pharm Investig. 2013 Oct;3(4):203-11. doi: 10.4103/2230-973X.121294. Int J Pharm Investig. 2013. PMID: 24350040 Free PMC article.
-
Use of fine particle ethylcellulose as the diluent in the production of pellets by extrusion-spheronization.Saudi Pharm J. 2014 Sep;22(4):360-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Nov 16. Saudi Pharm J. 2014. PMID: 25161381 Free PMC article.
-
Approaches to developing fast release pellets via wet extrusion-spheronization.Pharm Dev Technol. 2018 Jun;23(5):432-441. doi: 10.1080/10837450.2016.1265556. Epub 2016 Dec 9. Pharm Dev Technol. 2018. PMID: 27882815 Review.
-
A Review on Enteric Coated Pellets Composed of Core Pellets Prepared by Extrusion-Spheronization.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2019;13(2):83-90. doi: 10.2174/1872211313666190212115139. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2019. PMID: 30747090 Review.
Cited by
-
Microenvironmental pH-modified Amisulpride-Labrasol matrix tablets: development, optimization and in vivo pharmacokinetic study.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021 Feb;11(1):103-117. doi: 10.1007/s13346-019-00706-2. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 31900797
-
Implementing Central Composite Design for Developing Transdermal Diacerein-Loaded Niosomes: Ex vivo Permeation and In vivo Deposition.Curr Drug Deliv. 2018;15(9):1330-1342. doi: 10.2174/1567201815666180619105419. Curr Drug Deliv. 2018. PMID: 29921206 Free PMC article.
-
Nanosizing of a poorly soluble drug: technique optimization, factorial analysis, and pharmacokinetic study in healthy human volunteers.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014 Jun 17;9:2943-53. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S63395. eCollection 2014. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 24971006 Free PMC article.
-
Nanocrystals of Fusidic Acid for Dual Enhancement of Dermal Delivery and Antibacterial Activity: In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo Evaluation.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Feb 25;12(3):199. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12030199. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32106544 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle-Mediated Dual Targeting: An Approach for Enhanced Baicalin Delivery to the Liver.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Jan 29;12(2):107. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12020107. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32013203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murray MD, Haag KM, Black PK, Hall SD, Brater DC. Variable furosemide absorption and poor predictability of response in elderly patient. Pharmacotherapy. 1997;17:98–106. - PubMed
-
- Filippis PD, Zingone G, Gibellini M, Rubessa F, Rupena P. Dissolution rates of different drugs from solid dispersions with Eudragit RS. Eur J Pharm Sci. 1995;3(5):265–71.
-
- Otsuka M, Onoe M, Matsuda Y. Hygroscopic stability and dissolution properties of spray-dried solid dispersions of furosemide with eudragit. J Pharm Sci. 2006;82:32–8. - PubMed
-
- Boles Ponto LL, Schoenwald RD. Furosemide: A pharmacokinetic/ pharmacodynamic review part I. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1990;18:381–408. - PubMed
-
- Ozdmir N, Ordu S. Improvement of dissolution properties of furosemide by complexation with β -cyclodextrin. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1998;24:19–25. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

