Effect of a disintegration mechanism on wetting, water absorption, and disintegration time of orodispersible tablets
- PMID: 23112534
- PMCID: PMC3483525
- DOI: 10.4103/0975-1483.100021
Effect of a disintegration mechanism on wetting, water absorption, and disintegration time of orodispersible tablets
Abstract
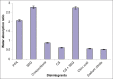
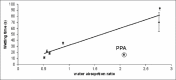
The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of disintegration mechanism of various types of disintegrants on the absorption ratio (AR), wetting time (WT), and disintegration time (DT) of orodispersible tablets (ODTs). ODTs were prepared by direct compression using mannitol as filler and disintegrants selected from a range of swellable, osmotic, and porous disintegrants. Tablets formed were characterized for their water AR, WT, and DT. The porosity and mechanical strength of the tablets were also measured. Results show that the DT of formulated ODTs was directly related to the WT and was a function of the disintegration mechanism of the disintegrant used. The lowest WT and DT were observed for tablets formulated using the osmotic disintegrant sodium citrate and these tablets also showed the lowest AR and porosity. The wetting and disintegration of tablets containing the highly swellable disintegrant, sodium starch glycollate, was slowest despite their high water AR and high tablet porosity. Rapid wetting and disintegration of ODTs were therefore not necessarily related to the porosity of the tablets.
Keywords: Absorption ratio; disintegration time; orodispersible tablets; porosity; wetting time.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of a superdisintegrant on disintegration of orally disintegrating tablets determined by simulated wetting test and in vitrodisintegration test.Pharmazie. 2022 Oct 1;77(10):287-290. doi: 10.1691/ph.2022.2015. Pharmazie. 2022. PMID: 36273260
-
Influence of Prosolv and Prosolv:Mannitol 200 direct compression fillers on the physicomechanical properties of atorvastatin oral dispersible tablets.Pharm Dev Technol. 2015 Jun;20(4):394-400. doi: 10.3109/10837450.2013.871031. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Pharm Dev Technol. 2015. PMID: 24397821
-
Understanding the mechanism for paradoxical effect of ionized and unionized chitosan: Orodispersible tablets of Ondansetron Hydrochloride.Pharm Dev Technol. 2009;14(5):476-84. doi: 10.1080/10837450902749279. Pharm Dev Technol. 2009. PMID: 19241220
-
Formulation of orodispersible tablets of ondansetron HCl: investigations using glycine-chitosan mixture as superdisintegrant.Yakugaku Zasshi. 2009 May;129(5):513-21. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.129.513. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2009. PMID: 19420882
-
Review of Disintegrants and the Disintegration Phenomena.J Pharm Sci. 2016 Sep;105(9):2545-2555. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2015.12.019. Epub 2016 Feb 12. J Pharm Sci. 2016. PMID: 27506604 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel sublingual tablets of Atorvastatin calcium/Trimetazidine hydrochloride combination; HPTLC quantification, in vitro formulation and characterization.Saudi Pharm J. 2019 May;27(4):540-549. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2019.02.001. Epub 2019 Feb 5. Saudi Pharm J. 2019. PMID: 31061623 Free PMC article.
-
Factorial analysis of the binding properties of acetylated ginger starch in metronidazole tablet formulations.Int J Pharm Investig. 2017 Jan-Mar;7(1):18-24. doi: 10.4103/jphi.JPHI_31_16. Int J Pharm Investig. 2017. PMID: 28405575 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Losartan Orally Disintegrating Tablets by Direct Compression: a Cost-Effective Approach to Improve Paediatric Patient's Compliance.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Apr 8;25(4):79. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02796-9. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38589718
-
Development and evaluation of Pleurotus tuber-regium-cornstarch composite as a direct compression multifunctional excipient.Int J Pharm Investig. 2016 Jan-Mar;6(1):10-22. doi: 10.4103/2230-973X.176461. Int J Pharm Investig. 2016. PMID: 27014615 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Robust Control Strategy for Fixed-Dose Combination Bilayer Tablets with Integrated Quality by Design, Statistical, and Process Analytical Technology Approach.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Sep 10;13(9):1443. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091443. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fu Y, Yang S, Jeong SH, Kimura S, Park K. Orally fast disintegrating tablets: Developments, technologies, taste-masking and clinical studies. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2004;21:433–76. - PubMed
-
- Sandri G, Bonferoni MC, Ferrari F, Rossi S, Caramella C. Differentiating factors between oral fast-dissolving technologies. Am J Drug Deliv. 2006;4:249–62.
-
- Seager H. Drug-delivery products and the Zydis fast-dissolving dosage form. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1998;50:375–82. - PubMed
-
- Klancke J. Dissolution testing of orally disintegrating tablets (CIMA LABS INC, Brooklyn Park, MN) Dissolut Technol. 2003;10:6–9.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

