An intelligent knowledge-based and customizable home care system framework with ubiquitous patient monitoring and alerting techniques
- PMID: 23112650
- PMCID: PMC3472878
- DOI: 10.3390/s120811154
An intelligent knowledge-based and customizable home care system framework with ubiquitous patient monitoring and alerting techniques
Abstract
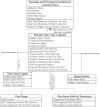
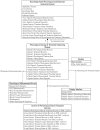
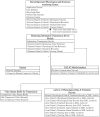
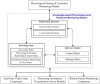
This study develops and integrates an efficient knowledge-based system and a component-based framework to design an intelligent and flexible home health care system. The proposed knowledge-based system integrates an efficient rule-based reasoning model and flexible knowledge rules for determining efficiently and rapidly the necessary physiological and medication treatment procedures based on software modules, video camera sensors, communication devices, and physiological sensor information. This knowledge-based system offers high flexibility for improving and extending the system further to meet the monitoring demands of new patient and caregiver health care by updating the knowledge rules in the inference mechanism. All of the proposed functional components in this study are reusable, configurable, and extensible for system developers. Based on the experimental results, the proposed intelligent homecare system demonstrates that it can accomplish the extensible, customizable, and configurable demands of the ubiquitous healthcare systems to meet the different demands of patients and caregivers under various rehabilitation and nursing conditions.
Keywords: Healthcare systems; component-based framework; handheld devices; knowledge-based systems; patient monitoring; ubiquitous monitoring.
Figures





References
-
- Kuo C.H., Huang F.G., Wang K.L., Lee M.Y., Chen H.W. Development of internet based remote health and activity monitoring systems for the elders. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2004;24:57–67.
-
- Kao W.C., Chen W.H., Yu C.K., Hong C.M., Lin S.Y. Portable real-time homecare system design with digital camera platform. IEEE Trans. Consumer Electron. 2005;51:1035–1041.
-
- Tai C.C., Chien J.R.C., Wang C.Y., Chen L.C., Chou C.H., Wu G.L. Infant monitoring system based on ARM embedded platform. Biomed. Eng. Appl. Basis. Comm. 2008;20:269–275.
-
- Pavlopoulos S., Kyriacou E., Berler A., Dembeyiotis S., Koutsouris D. A novel emergency telemedicine system based on wireless communication technology-AMBULANCE. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 1998;2:261–267. - PubMed
-
- Suresh D., Alli P. An overview of research issues in the modern healthcare monitoring system design using wireless body area network. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2012;9:54–59.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

