Efficient security mechanisms for mHealth applications using wireless body sensor networks
- PMID: 23112734
- PMCID: PMC3478861
- DOI: 10.3390/s120912606
Efficient security mechanisms for mHealth applications using wireless body sensor networks
Abstract
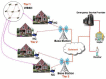
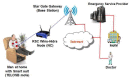
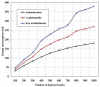
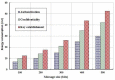
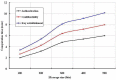
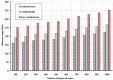
Recent technological advances in wireless communications and physiological sensing allow miniature, lightweight, ultra-low power, intelligent monitoring devices, which can be integrated into a Wireless Body Sensor Network (WBSN) for health monitoring. Physiological signals of humans such as heartbeats, temperature and pulse can be monitored from a distant location using tiny biomedical wireless sensors. Hence, it is highly essential to combine the ubiquitous computing with mobile health technology using wireless sensors and smart phones to monitor the well-being of chronic patients such as cardiac, Parkinson and epilepsy patients. Since physiological data of a patient are highly sensitive, maintaining its confidentiality is highly essential. Hence, security is a vital research issue in mobile health (mHealth) applications, especially if a patient has an embarrassing disease. In this paper a three tier security architecture for the mHealth application is proposed, in which light weight data confidentiality and authentication protocols are proposed to maintain the privacy of a patient. Moreover, considering the energy and hardware constraints of the wireless body sensors, low complexity data confidential and authentication schemes are designed. Performance evaluation of the proposed architecture shows that they can satisfy the energy and hardware limitations of the sensors and still can maintain the secure fabrics of the wireless body sensor networks. Besides, the proposed schemes can outperform in terms of energy consumption, memory usage and computation time over standard key establishment security scheme.
Keywords: authentication; confidentiality; mHealth; security; wireless body sensor networks.
Figures







References
-
- Implementing e-Health in Developing Countries. Available online: http://www.itu.int/ITU-D/cyb/app/docs/e-Health-prefinal-15092008.PDF (accessed on 8 March 2012)
-
- US Edge An IT Resource You can Trust. Available online: http://www.mobih.org/ (accessed on 8 March 2012)
-
- Chakravorty R. A Programmable Service Architecture for Mobile Medical Care. Proceedings of the 4th Annual IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communication Workshop (PERSOMW '06); Pisa, Italy. 13– 17 March 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

