Mutual information rate and bounds for it
- PMID: 23112809
- PMCID: PMC3480398
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046745
Mutual information rate and bounds for it
Abstract
The amount of information exchanged per unit of time between two nodes in a dynamical network or between two data sets is a powerful concept for analysing complex systems. This quantity, known as the mutual information rate (MIR), is calculated from the mutual information, which is rigorously defined only for random systems. Moreover, the definition of mutual information is based on probabilities of significant events. This work offers a simple alternative way to calculate the MIR in dynamical (deterministic) networks or between two time series (not fully deterministic), and to calculate its upper and lower bounds without having to calculate probabilities, but rather in terms of well known and well defined quantities in dynamical systems. As possible applications of our bounds, we study the relationship between synchronisation and the exchange of information in a system of two coupled maps and in experimental networks of coupled oscillators.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

 and in (B)
and in (B)  . The units of
. The units of  ,
,  , and
, and  are [bits/iteration].
are [bits/iteration].
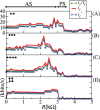
 as (green online) filled circles,
as (green online) filled circles,  as the (red online) thick line, and
as the (red online) thick line, and  as the (blue online) squares, for a varying coupling resistance
as the (blue online) squares, for a varying coupling resistance  . The unit of these quantities shown in these figures is (kbits/s). (A) Topology I, (B) Topology II, (C) Topology III, and (D) Topology IV. In all figures,
. The unit of these quantities shown in these figures is (kbits/s). (A) Topology I, (B) Topology II, (C) Topology III, and (D) Topology IV. In all figures,  increases smoothly from 1.25 to 1.95 as
increases smoothly from 1.25 to 1.95 as  varies from 0.1k
varies from 0.1k to 5k
to 5k . The line on the top of the figure represents the interval of resistance values responsible to induce almost synchronisation (AS) and phase synchronisation (PS).
. The line on the top of the figure represents the interval of resistance values responsible to induce almost synchronisation (AS) and phase synchronisation (PS).
 the points do not spread any longer (D).
the points do not spread any longer (D).Similar articles
-
Information-Theoretic Bounds and Approximations in Neural Population Coding.Neural Comput. 2018 Apr;30(4):885-944. doi: 10.1162/neco_a_01056. Epub 2018 Jan 17. Neural Comput. 2018. PMID: 29342399 Free PMC article.
-
A model of gene expression based on random dynamical systems reveals modularity properties of gene regulatory networks.Math Biosci. 2016 Jun;276:82-100. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2016.03.008. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Math Biosci. 2016. PMID: 27036626
-
Bounds on the rates of statistical divergences and mutual information via stochastic thermodynamics.Phys Rev E. 2024 May;109(5-1):054126. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.109.054126. Phys Rev E. 2024. PMID: 38907417
-
Information theory and signal transduction systems: from molecular information processing to network inference.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Nov;35:98-108. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.06.011. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24953199 Review.
-
Boolean network models of cellular regulation: prospects and limitations.J R Soc Interface. 2008 Aug 6;5 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S85-94. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2008.0132.focus. J R Soc Interface. 2008. PMID: 18508746 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chaotic, informational and synchronous behaviour of multiplex networks.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 4;6:22617. doi: 10.1038/srep22617. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26939580 Free PMC article.
-
Do Brain Networks Evolve by Maximizing Their Information Flow Capacity?PLoS Comput Biol. 2015 Aug 28;11(8):e1004372. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004372. eCollection 2015 Aug. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015. PMID: 26317592 Free PMC article.
-
Markovian language model of the DNA and its information content.R Soc Open Sci. 2016 Jan 6;3(1):150527. doi: 10.1098/rsos.150527. eCollection 2016 Jan. R Soc Open Sci. 2016. PMID: 26909179 Free PMC article.
-
Production and transfer of energy and information in Hamiltonian systems.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 28;9(2):e89585. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089585. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586891 Free PMC article.
-
Inference of financial networks using the normalised mutual information rate.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 8;13(2):e0192160. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192160. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29420644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shannon CE (1948) A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell System Technical Journal 27: 379–423.
-
- Strong SP, Koberle R, de Ruyter van Steveninck RR, Bialek W (1998) Entropy and Information in Neural Spike Trains. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80: 197–200.
-
- Sporns O, Chialvo DR, Kaiser M, Hilgetag CC (2004) Organization, development and function of complex brain networks. Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 8: 418–425. - PubMed
-
- Palus M, Komárek V, Procházka T, Hrncir Z, Sterbova K (2001) Synchronization and information ow in EEGs of epileptic patients. IEEE Engineering in Medicice and Biology Sep/Oct: 65–71. - PubMed
-
- Donges JF, Zou Y, Marwan N, Kurths J (2009) Complex networks in climate dynamics. Eur. Phys. J. 174: 157–179.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

