Upregulation of the Tim-3/galectin-9 pathway of T cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis B virus infection
- PMID: 23112829
- PMCID: PMC3480425
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047648
Upregulation of the Tim-3/galectin-9 pathway of T cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis B virus infection
Abstract
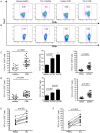
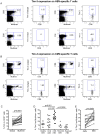
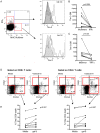
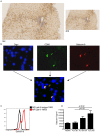
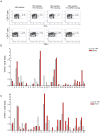
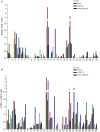
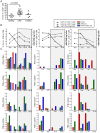
The S-type lectin galectin-9 binds to the negative regulatory molecule Tim-3 on T cells and induces their apoptotic deletion or functional inactivation. We investigated whether galectin-9/Tim-3 interactions contribute to the deletion and exhaustion of the antiviral T cell response in chronic hepatitis B virus infection (CHB). We found Tim-3 to be expressed on a higher percentage of CD4 and CD8 T cells from patients with CHB than healthy controls (p<0.0001) and to be enriched on activated T cells and those infiltrating the HBV-infected liver. Direct ex vivo examination of virus-specific CD8 T cells binding HLA-A2/peptide multimers revealed that Tim-3 was more highly upregulated on HBV-specific CD8 T cells than CMV-specific CD8 T cells or the global CD8 T cell population in patients with CHB (p<0.001) or than on HBV-specific CD8 after resolution of infection. T cells expressing Tim-3 had an impaired ability to produce IFN-γ and TNF-α upon recognition of HBV-peptides and were susceptible to galectin-9-triggered cell death in vitro. Galectin-9 was detectable at increased concentrations in the sera of patients with active CHB-related liver inflammation (p = 0.02) and was strongly expressed by Kupffer cells within the liver sinusoidal network. Tim-3 blockade resulted in enhanced expansion of HBV-specific CD8 T cells able to produce cytokines and mediate cytotoxicity in vitro. Blocking PD-1 in combination with Tim-3 enhanced the number of patients from whom functional antiviral responses could be recovered and/or the strength of responses, indicating that these co-inhibitory molecules play a non-redundant role in driving T cell exhaustion in CHB. Patients taking antivirals able to potently suppress HBV viraemia continued to express Tim-3 on their T cells and respond to Tim-3 blockade. In summary, both Tim-3 and galectin-9 are increased in CHB and may contribute to the inhibition and deletion of T cells as they infiltrate the HBV-infected liver.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Rabinovich GA, Toscano MA (2009) Turning ‘sweet’ on immunity: galectin-glycan interactions in immune tolerance and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 9: 338–352. - PubMed
-
- Monney L, Sabatos CA, Gaglia JL, Ryu A, Waldner H, et al. (2002) Th1-specific cell surface protein Tim-3 regulates macrophage activation and severity of an autoimmune disease. Nature 415: 536–541. - PubMed
-
- Zhu C, Anderson AC, Schubart A, Xiong H, Imitola J, et al. (2005) The Tim-3 ligand galectin-9 negatively regulates T helper type 1 immunity. Nat Immunol 6: 1245–1252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

