Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase regulates the motility of breast cancer cells
- PMID: 23112838
- PMCID: PMC3480402
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047721
Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase regulates the motility of breast cancer cells
Abstract
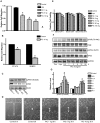
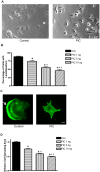
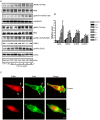
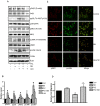
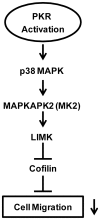
Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-dependent protein kinase (PKR) is an interferon-induced protein kinase that plays a central role in the anti-viral process. Due to its pro-apoptotic and anti-proliferative action, there is an increased interest in PKR modulation as an anti-tumor strategy. PKR is overexpressed in breast cancer cells; however, the role of PKR in breast cancer cells is unclear. The expression/activity of PKR appears inversely related to the aggressiveness of breast cancer cells. The current study investigated the role of PKR in the motility/migration of breast cancer cells. The activation of PKR by a synthesized dsRNA (PIC) significantly decreased the motility of several breast cancer cell lines (BT474, MDA-MB231 and SKBR3). PIC inhibited cell migration and blocked cell membrane ruffling without affecting cell viability. PIC also induced the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and impaired the formation of lamellipodia. These effects of PIC were reversed by the pretreatment of a selective PKR inhibitor. PIC also activated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and its downstream MAPK-activated protein kinase 2 (MK2). PIC-induced activation of p38 MAPK and MK2 was attenuated by the PKR inhibitor and the PKR siRNA, but a selective p38 MAPK inhibitor (SB203580) or other MAPK inhibitors did not affect PKR activity, indicating that PKR is upstream of p38 MAPK/MK2. Cofilin is an actin severing protein and regulates membrane ruffling, lamellipodia formation and cell migration. PIC inhibited cofilin activity by enhancing its phosphorylation at Ser3. PIC activated LIM kinase 1 (LIMK1), an upstream kinase of cofilin in a p38 MAPK-dependent manner. We concluded that the activation of PKR suppressed cell motility by regulating the p38 MAPK/MK2/LIMK/cofilin pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
MAPKAPK-2-mediated LIM-kinase activation is critical for VEGF-induced actin remodeling and cell migration.EMBO J. 2006 Feb 22;25(4):713-26. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600973. Epub 2006 Feb 2. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16456544 Free PMC article.
-
The p38/MK2/Hsp25 pathway is required for BMP-2-induced cell migration.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 28;6(1):e16477. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016477. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21297993 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic deletion of PKR abrogates TNF-induced activation of IkappaBalpha kinase, JNK, Akt and cell proliferation but potentiates p44/p42 MAPK and p38 MAPK activation.Oncogene. 2007 Feb 22;26(8):1201-12. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209906. Epub 2006 Aug 21. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 16924232
-
Roles of protein kinase R in cancer: Potential as a therapeutic target.Cancer Sci. 2018 Apr;109(4):919-925. doi: 10.1111/cas.13551. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 29478262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PKR/P38/RIPK1 Signaling Pathway as a Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 19;22(6):3136. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063136. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33808629 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Antiviral Compound PSP Inhibits HIV-1 Entry via PKR-Dependent Activation in Monocytic Cells.Viruses. 2023 Mar 22;15(3):804. doi: 10.3390/v15030804. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992512 Free PMC article.
-
Zebularine upregulates expression of CYP genes through inhibition of DNMT1 and PKR in HepG2 cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 23;7:41093. doi: 10.1038/srep41093. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28112215 Free PMC article.
-
Cofilin activation in pancreatic acinar cells plays a pivotal convergent role for mediating CCK-stimulated enzyme secretion and growth.Front Physiol. 2023 Apr 17;14:1147572. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1147572. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37138671 Free PMC article.
-
PACT/RAX regulates the migration of cerebellar granule neurons in the developing cerebellum.Sci Rep. 2015 Jan 22;5:7961. doi: 10.1038/srep07961. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25609658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Williams BR (2001) Signal integration via PKR. Sci STKE 2001: re2. 10.1126/stke.2001.89.re2 [doi];2001/89/re2 [pii]. - PubMed
-
- Vorburger SA, Pataer A, Swisher SG, Hunt KK (2004) Genetically targeted cancer therapy: tumor destruction by PKR activation. Am J Pharmacogenomics 4: 189–198. 436 [pii]. - PubMed
-
- Balachandran S, Barber GN (2007) PKR in innate immunity, cancer, and viral oncolysis. Methods Mol Biol 383: 277–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

