The Effect of Different Intrathecal Doses of Meperidine on Shivering during Delivery Under Spinal Anesthesia
- PMID: 23112897
- PMCID: PMC3482998
The Effect of Different Intrathecal Doses of Meperidine on Shivering during Delivery Under Spinal Anesthesia
Abstract
Background: This study was performed to compare the effect of different doses of intrathecal meperidine on the incidence and intensity of shivering and other side-effects after spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery.
Methods: One hundred and fifty-six parturient women scheduled for elective cesarean delivery were enrolled in four groups. Spinal anesthesia consisted of heavy bupivacaine 0.5% (10 mg) in the standard group (Group I), heavy bupivacaine 0.5% (10 mg) plus meperidine (0.2 mg per kg) in Group II, heavy bupivacaine 0.5% (10 mg) plus meperidine (0.3 mg per kg) in Group III, heavy bupivacaine 0.5% (10 mg) plus meperidine (0.4 mg per kg) in Group IV. The signs and symptoms were recorded by an observer unaware of the study groups. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance, Kruskal-Wallis H-test and chi-square. A P value less than 0.05 was considered to be significant.
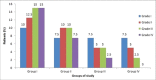
Results: The systolic blood pressure, amount of bleeding, Pulse Rate, O2 saturation, neonatal apgar scores, core temperatures and sensory level revealed no difference between groups (P>0.05). The incidence (47.5%, 37.5%, 27.5% and 15.0%, respectively) and intensity of shivering decreased as the dose of meperidine increased (P=0.002) but the incidence of nausea and vomiting (8.0%, 15.4%, 25.9% and 35.8%, respectively) (P=0.000) and pruritis (25.64, 28.21, 38.46, and 48.72 respectively) increased as the dose of meperidine increased (P=0.000).
Conclusion: The high dose of intrathecal meperidine is effective in reducing the incidence and intensity of shivering associated with spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery but the high incidence of nausea and vomiting is unpleasant for the patient and can be a major problem with a high dose of meperdine.
Keywords: Bupivacaine 0.5%; delivery; intrathecal; meperidine; shivering.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of low dose of intrathecal pethidine on the incidence and intensity of shivering during cesarean section under spinal anesthesia: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Sep 20;10:3005-3012. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S115201. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 27703328 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Preventing shivering with adjuvant low dose intrathecal meperidine: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials with trial sequential analysis.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 10;7(1):15323. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14917-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29127294 Free PMC article.
-
Intrathecal meperidine decreases shivering during cesarean delivery under spinal anesthesia.Anesth Analg. 2004 Jan;98(1):230-234. doi: 10.1213/01.ANE.0000093251.42341.74. Anesth Analg. 2004. PMID: 14693625 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of warm and cold intrathecal bupivacaine on shivering during delivery under spinal anesthesia.Saudi J Anaesth. 2012 Oct-Dec;6(4):336-40. doi: 10.4103/1658-354X.105854. Saudi J Anaesth. 2012. PMID: 23493460 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Intrathecal Fentanyl for Cesarean Delivery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials With Trial Sequential Analysis.Anesth Analg. 2020 Jan;130(1):111-125. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000003975. Anesth Analg. 2020. PMID: 30633056
Cited by
-
Efficiency and safety of ondansetron in preventing postanaesthesia shivering.Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2016 Jul;98(6):358-66. doi: 10.1308/rcsann.2016.0152. Epub 2016 May 3. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2016. PMID: 27138855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of clinical effects of meperidine and sufentanil added to 0.5% hyperbaric bupivacaine for spinal anesthesia in patients undergoing cesarean delivery: a randomized controlled trial.J Anesth. 2022 Apr;36(2):201-209. doi: 10.1007/s00540-021-03031-6. Epub 2022 Jan 27. J Anesth. 2022. PMID: 35083557 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of low dose of intrathecal pethidine on the incidence and intensity of shivering during cesarean section under spinal anesthesia: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Sep 20;10:3005-3012. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S115201. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 27703328 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Preventing shivering with adjuvant low dose intrathecal meperidine: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials with trial sequential analysis.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 10;7(1):15323. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14917-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29127294 Free PMC article.
-
Neuraxial adjuvants for prevention of perioperative shivering during cesarean section: A network meta-analysis following the PRISMA guidelines.World J Clin Cases. 2019 Aug 26;7(16):2287-2301. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i16.2287. World J Clin Cases. 2019. PMID: 31531322 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crowley LJ, Buggy DJ. Shivering and neuraxialanaesthesia. RegAnesth Pain Med. 2008;33:241–52. - PubMed
-
- De Witte J, Sessler DI. Perioperative shivering: Physiology and pharmacology. Anesthesiology. 2002;96:467–84. - PubMed
-
- Han JW, Kang HS, Choi SK, Park SJ, Park HJ, Lim TH. Comparison of the effects of intrathecal fentanyl and meperidine on shivering after cesarean delivery under spinal anaesthesia. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2007;52:657–62.
-
- Chaney M. Side effects of intrathecal and epidural opioids. Can J Anaesth. 1995;42:891–903. - PubMed
-
- Roy J-D, Girard M, Drolet P. Intrathecalmeperidine decreases shivering during cesarean delivery under spinal anesthesia. AnesthAnalg. 2004;98:230–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources