Role of conformational dynamics in α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA) receptor partial agonism
- PMID: 23115239
- PMCID: PMC3527942
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.371815
Role of conformational dynamics in α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA) receptor partial agonism
Abstract
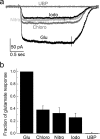
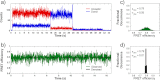
We have investigated the range of cleft closure conformational states that the agonist-binding domains of the α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA) receptors occupy when bound to a series of willardiine derivatives using single-molecule FRET. These studies show that the agonist-binding domain exhibits varying degrees of dynamics when bound to the different willardiines with differing efficacies. The chlorowillardiine- and nitrowillardiine-bound form of the agonist-binding domain probes a narrower range of cleft closure states relative to the iodowillardiine bound form of the protein, with the antagonist (αS)-α-amino-3-[(4-carboxyphenyl)methyl]-3,4-dihydro-2,4-dioxo-1(2H)-pyrimidinepropanoic acid (UBP-282)-bound form exhibiting the widest range of cleft closure states. Additionally, the average cleft closure follows the order UBP-282 > iodowillardiine > chlorowillardiine > nitrowillardiine-bound forms of agonist-binding domain. These single-molecule FRET data, along with our previously reported data for the glutamate-bound forms of wild type and T686S mutant proteins, show that the mean currents under nondesensitizing conditions can be directly correlated to the fraction of the agonist-binding domains in the "closed" cleft conformation. These results indicate that channel opening in the AMPA receptors is controlled by both the ability of the agonist to induce cleft closure and the dynamics of the agonist-binding domain when bound to the agonist.
Figures



References
-
- Nakanishi S. (1992) Molecular diversity of glutamate receptors and implications for brain function. Science 258, 597–603 - PubMed
-
- Nakanishi S., Masu M. (1994) Molecular diversity and functions of glutamate receptors. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 23, 319–348 - PubMed
-
- Madden D. R. (2002) The structure and function of glutamate receptor ion channels. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 91–101 - PubMed
-
- McFeeters R. L., Oswald R. E. (2004) Emerging structural explanations of ionotropic glutamate receptor function. FASEB J. 18, 428–438 - PubMed
-
- Valentine E. R., Palmer A. G., 3rd. (2005) Microsecond-to-millisecond conformational dynamics demarcate the GluR2 glutamate receptor bound to agonists glutamate, quisqualate, and AMPA. Biochemistry 44, 3410–3417 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

