The highest attainable standard of evidence (HASTE) for HIV/AIDS interventions: toward a public health approach to defining evidence
- PMID: 23115382
- PMCID: PMC3461350
- DOI: 10.1177/003335491212700607
The highest attainable standard of evidence (HASTE) for HIV/AIDS interventions: toward a public health approach to defining evidence
Abstract
Objectives: Evidence-driven decisions have become a standard for health interventions, policy, and programs. While randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are encouraged for public health interventions, there are limitations with RCTs as the gold standard of evidence for HIV interventions. We developed a novel system of evaluating evidence for assessing HIV preventive interventions termed the Highest Attainable Standard of Evidence (HASTE).
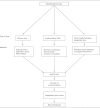
Methods: The HASTE system focuses on triangulation of three distinct categories of evidence: efficacy data, implementation data, and plausibility. We conducted systematic reviews, including experimental and observational data, to assess all available interventions for men who have sex with men (MSM). We collected implementation and programmatic data using a global electronic consultation, Internet searches, and in-person consultations. We assessed plausibility with expert analyses of both biological and public health evidence.
Results: HASTE includes four grades of evidence: Strong (Grade 1), Conditional (Grade 2), Insufficient (Grade 3), and Inappropriate (Grade 4). We used the HASTE system to evaluate the evidence for HIV interventions for MSM in low- and middle-income countries. Several differences emerged in the strength of recommendation with the use of the HASTE system, including strong recommendations for voluntary counseling and testing and for structural interventions.
Conclusions: The HASTE system addresses a need for an evidence evaluation tool that is specific for HIV interventions and facilitates an evaluation of biomedical, behavioral, and structural approaches using the highest standard of attainable evidence. HASTE represents a tool that balances scientific integrity and practicality in assessing the quality of evidence of preventive interventions targeting the most-at-risk populations for HIV.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
A social systems analysis of implementation of El Salvador's national HIV combination prevention: a research agenda for evaluating Global Health Initiatives.BMC Health Serv Res. 2018 Nov 12;18(1):848. doi: 10.1186/s12913-018-3667-8. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018. PMID: 30419904 Free PMC article.
-
The Effectiveness of Electronic Health Interventions for Promoting HIV-Preventive Behaviors Among Men Who Have Sex With Men: Meta-Analysis Based on an Integrative Framework of Design and Implementation Features.J Med Internet Res. 2020 May 25;22(5):e15977. doi: 10.2196/15977. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32449685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Application of " Internet Plus" AIDS prevention services among men who have sex with men in Guangzhou, China: results from 2010 to 2015].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Oct 6;50(10):853-857. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2016.10.004. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27686761 Chinese.
-
HIV sexual risk reduction interventions for women: a review.Am J Prev Med. 1996 May-Jun;12(3):209-17. Am J Prev Med. 1996. PMID: 8743877 Review.
Cited by
-
Rating the quality of a body of evidence on the effectiveness of health and social interventions: A systematic review and mapping of evidence domains.Res Synth Methods. 2018 Jun;9(2):224-242. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1290. Epub 2018 Mar 2. Res Synth Methods. 2018. PMID: 29346709 Free PMC article.
-
Global variation in antibiotic prescribing guidelines and the implications for decreasing AMR in the future.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Aug 7;16:1600787. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1600787. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40852607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIV-Related Implementation Research for Key Populations: Designing for Individuals, Evaluating Across Populations, and Integrating Context.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2019 Dec;82 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S206-S216. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002191. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2019. PMID: 31764256 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of interventions to reduce HIV-related stigma and discrimination from 2002 to 2013: how far have we come?J Int AIDS Soc. 2013 Nov 13;16(3 Suppl 2):18734. doi: 10.7448/IAS.16.3.18734. J Int AIDS Soc. 2013. PMID: 24242268 Free PMC article.
-
A Randomized Clinical Trial of a Brief Internet-based Group Intervention to Reduce Sexual Transmission Risk Behavior Among HIV-Positive Gay and Bisexual Men.Ann Behav Med. 2018 Feb 5;52(2):116-129. doi: 10.1093/abm/kax031. Ann Behav Med. 2018. PMID: 29538626 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Wolfe D, Carrieri MP, Shepard D. Treatment and care for injecting drug users with HIV infection: a review of barriers and ways forward. Lancet. 2010;376:355–66. - PubMed
-
- Degenhardt L, Mathers B, Vickerman P, Rhodes T, Latkin C, Hickman M. Prevention of HIV infection for people who inject drugs: why individual, structural, and combination approaches are needed. Lancet. 2010;376:285–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical