Deep Brain Stimulation of the Globus Pallidus in a 7-Year-Old Girl with DYT1 Generalized Dystonia
- PMID: 23115674
- PMCID: PMC3483332
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2012.52.3.261
Deep Brain Stimulation of the Globus Pallidus in a 7-Year-Old Girl with DYT1 Generalized Dystonia
Abstract
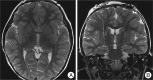
The experience of pediatric deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the globus pallidus internus (GPi) in the treatment of early-onset DYT1 generalized dystonia is still limited. Here, we report the surgical experience of bilateral GPi-DBS under general anesthesia by using microelectrode recording in a 7-year-old girl with early-onset DYT1 generalized dystonia. Excellent improvement of her dystonia without neurological complications was achieved. This case report demonstrates that GPi-DBS is an effective and safe method for the treatment of medically refractory early-onset DYT1 generalized dystonia in children.
Keywords: DYT1; Deep brain stimulation; Dystonia; Globus pallidus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chronic stimulation of the globus pallidus internus for treatment of non-dYT1 generalized dystonia and choreoathetosis: 2-year follow up.J Neurosurg. 2003 Apr;98(4):785-92. doi: 10.3171/jns.2003.98.4.0785. J Neurosurg. 2003. PMID: 12691403
-
Deep brain stimulation of globus pallidus internus for DYT1 positive primary generalized dystonia.Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2014 Mar 1;28:18. eCollection 2014. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2014. PMID: 25250263 Free PMC article.
-
Two Cases of Monozygotic Twins with Early-onset Isolated (DYT1) Dystonia Effectively Treated with Bilateral Globus Pallidus Internus Stimulation.NMC Case Rep J. 2022 Sep 15;9:307-312. doi: 10.2176/jns-nmc.2022-0084. eCollection 2022. NMC Case Rep J. 2022. PMID: 36263189 Free PMC article.
-
Pallidal Deep Brain Stimulation for Monogenic Dystonia: The Effect of Gene on Outcome.Front Neurol. 2021 Jan 8;11:630391. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.630391. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33488508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep brain stimulation for torsion dystonia.Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2007;97(Pt 2):191-9. doi: 10.1007/978-3-211-33081-4_21. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2007. PMID: 17691304 Review.
Cited by
-
Deep brain stimulation in pediatric dystonia: a systematic review.Neurosurg Rev. 2020 Jun;43(3):873-880. doi: 10.1007/s10143-018-1047-9. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Neurosurg Rev. 2020. PMID: 30397842 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of general anesthesia deep brain stimulation for dystonia: an individual patient data meta-analysis of 341 cases.Neurol Sci. 2021 Jul;42(7):2661-2671. doi: 10.1007/s10072-021-05214-1. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Neurol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33855621 Review.
References
-
- Alterman RL, Tagliati M. Deep brain stimulation for torsion dystonia in children. Childs Nerv Syst. 2007;23:1033–1040. - PubMed
-
- Augood SJ, Penney JB, Jr, Friberg IK, Breakefield XO, Young AB, Ozelius LJ, et al. Expression of the early-onset torsion dystonia gene (DYT1) in human brain. Ann Neurol. 1998;43:669–673. - PubMed
-
- Constantoyannis C, Berk C, Honey CR, Mendez I, Brownstone RM. Reducing hardware-related complications of deep brain stimulation. Can J Neurol Sci. 2005;32:194–200. - PubMed
-
- Coubes P, Cif L, El Fertit H, Hemm S, Vayssiere N, Serrat S, et al. Electrical stimulation of the globus pallidus internus in patients with primary generalized dystonia : long-term results. J Neurosurg. 2004;101:189–194. - PubMed
-
- Dekaban AS. Changes in brain weights during the span of human life : relation of brain weights to body heights and body weights. Ann Neurol. 1978;4:345–356. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

