Function of members of the neuropilin family as essential pleiotropic cell surface receptors
- PMID: 23116416
- PMCID: PMC3510667
- DOI: 10.1021/bi3012143
Function of members of the neuropilin family as essential pleiotropic cell surface receptors
Abstract
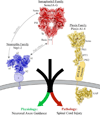
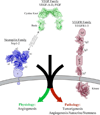
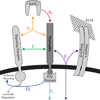
The neuropilin (Nrp) family consists of essential multifunctional vertebrate cell surface receptors. Nrps were initially characterized as receptors for class III Semaphorin (Sema3) family members, functioning in axon guidance. Nrps have also been shown to be critical for vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent angiogenesis. Intriguingly, recent data show that Nrp function in these seemingly divergent pathways is critically determined by ligand-mediated cross-talk, which underlies Nrp function in both physiological and pathological processes. In addition to functioning in these two pathways, Nrps have been shown to specifically function in a number of other fundamental signaling pathways as well. Multiple general mechanisms have been found to directly contribute to the pleiotropic function of Nrp. Here we review critical general features of Nrps that function as essential receptors integrating multiple molecular cues into diverse cellular signaling.
Figures

References
-
- Takagi S, Tsuji T, Amagai T, Takamatsu T, Fujisawa H. Specific cell surface labels in the visual centers of Xenopus laevis tadpole identified using monoclonal antibodies. Dev Biol. 1987;122:90–100. - PubMed
-
- Takagi S, Hirata T, Agata K, Mochii M, Eguchi G, Fujisawa H. The A5 antigen, a candidate for the neuronal recognition molecule, has homologies to complement components and coagulation factors. Neuron. 1991;7:295–307. - PubMed
-
- Kolodkin AL, Levengood DV, Rowe EG, Tai YT, Giger RJ, Ginty DD. Neuropilin is a semaphorin III receptor. Cell. 1997;90:753–762. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Chedotal A, He Z, Goodman CS, Tessier-Lavigne M. Neuropilin-2, a novel member of the neuropilin family, is a high affinity receptor for the semaphorins Sema E and Sema IV but not Sema III. Neuron. 1997;19:547–559. - PubMed
-
- Gaboriaud C, Gregory-Pauron L, Teillet F, Thielens NM, Bally I, Arlaud GJ. Structure and properties of the Ca(2+)-binding CUB domain, a widespread ligand-recognition unit involved in major biological functions. Biochem J. 2011;439:185–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

