SKA-31, a novel activator of SK(Ca) and IK(Ca) channels, increases coronary flow in male and female rat hearts
- PMID: 23118129
- PMCID: PMC3543990
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvs326
SKA-31, a novel activator of SK(Ca) and IK(Ca) channels, increases coronary flow in male and female rat hearts
Abstract
Aims: Endothelial SK(Ca) and IK(Ca) channels play an important role in the regulation of vascular function and systemic blood pressure. Based on our previous findings that small molecule activators of SK(Ca) and IK(Ca) channels (i.e. NS309 and SKA-31) can inhibit myogenic tone in isolated resistance arteries, we hypothesized that this class of compounds may induce effective vasodilation in an intact vascular bed, such as the coronary circulation.
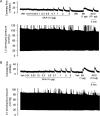
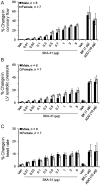
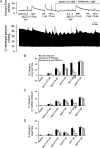
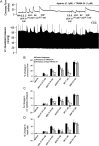
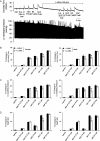
Methods and results: In a Langendorff-perfused, beating rat heart preparation, acute bolus administrations of SKA-31 (0.01-5 µg) dose-dependently increased total coronary flow (25-30%) in both male and female hearts; these responses were associated with modest, secondary increases in left ventricular (LV) systolic pressure and heart rate. SKA-31 evoked responses in coronary flow, LV pressure, and heart rate were qualitatively comparable to acute responses evoked by bradykinin (1 µg) and adenosine (10 µg). In the presence of apamin and TRAM-34, selective blockers of SK(Ca) and IK(Ca) channels, respectively, SKA-31 and bradykinin-induced responses were largely inhibited, whereas the adenosine-induced changes were blocked by ∼40%; TRAM-34 alone produced less inhibition. Sodium nitroprusside (SNP, 0.2 μg bolus dose) evoked changes in coronary flow, LV pressure, and heart rate were similar to those induced by SKA-31, but were unaffected by apamin + TRAM-34. The NOS inhibitor L-NNA reduced bradykinin- and adenosine-evoked changes, but did not affect responses to either SKA-31 or SNP.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that SKA-31 can rapidly and reversibly induce dilation of the coronary circulation in intact functioning hearts under basal flow and contractility conditions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A pharmacologic activator of endothelial KCa channels enhances coronary flow in the hearts of type 2 diabetic rats.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Jul;72:364-73. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.04.013. Epub 2014 Apr 29. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24787473
-
Vascular Reactivity Profile of Novel KCa 3.1-Selective Positive-Gating Modulators in the Coronary Vascular Bed.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016 Aug;119(2):184-92. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.12560. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26821335 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological activation of small conductance calcium-activated potassium channels with naphtho[1,2-d]thiazol-2-ylamine decreases guinea pig detrusor smooth muscle excitability and contractility.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Jan;340(1):114-23. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.186213. Epub 2011 Oct 14. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 22001258 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacologic targeting of endothelial Ca2+-activated K+ channels: A strategy to improve cardiovascular function.Channels (Austin). 2018 Jan 1;12(1):126-136. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2018.1454814. Channels (Austin). 2018. PMID: 29577810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelium-derived hyperpolarising factors and associated pathways: a synopsis.Pflugers Arch. 2010 May;459(6):863-79. doi: 10.1007/s00424-010-0817-1. Epub 2010 Apr 11. Pflugers Arch. 2010. PMID: 20383718 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological Targeting of KCa Channels to Improve Endothelial Function in the Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 16;20(14):3481. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143481. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31315169 Free PMC article.
-
Preserved regulation of renal perfusion pressure by small and intermediate conductance KCa channels in hypertensive mice with or without renal failure.Pflugers Arch. 2015 Apr;467(4):817-31. doi: 10.1007/s00424-014-1542-y. Epub 2014 Jun 7. Pflugers Arch. 2015. PMID: 24903240
-
Endothelial KCa channels: Novel targets to reduce atherosclerosis-driven vascular dysfunction.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 31;14:1151244. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1151244. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37063294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of endothelial transient receptor potential C3 channel is required for small conductance calcium-activated potassium channel activation and sustained endothelial hyperpolarization and vasodilation of cerebral artery.J Am Heart Assoc. 2014 Aug 20;3(4):e000913. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.114.000913. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014. PMID: 25142058 Free PMC article.
-
A novel pan-negative-gating modulator of KCa2/3 channels, fluoro-di-benzoate, RA-2, inhibits endothelium-derived hyperpolarization-type relaxation in coronary artery and produces bradycardia in vivo.Mol Pharmacol. 2015 Feb;87(2):338-48. doi: 10.1124/mol.114.095745. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Mol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25468883 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Busse R, Fleming I, Hecker M. Signal transduction in endothelium-dependent vasodilatation. Eur Heart J. 1993;14(Suppl.1):2–9. - PubMed
-
- Busse R, Edwards G, Félétou M, Fleming I, Vanhoutte PM, Weston AH. EDHF: bringing the concepts together. TIPS. 2002;23:374–380. - PubMed
-
- Grgic I, Kaistha A, Hoyer J, Köhler R. Endothelial Ca2+-activated K+ channels in normal and impaired EDHF-dilator responses—relevance to cardiovascular pathologies and drug discovery. Br J Pharmacol. 2009;157:509–526. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00132.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Edwards G, Félétou M, Weston AH. Endothelium-derived hyperpolarising factors and associated pathways: a synopsis. Pflügers Arch. 2010;459:863–879. doi:10.1007/s00424-010-0817-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sheng J-Z, Braun AP. Small- and intermediate-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels directly control agonist-evoked nitric oxide synthesis in human vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;293:C458–C467. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00036.2007. - DOI - PubMed

