Proteomic analysis of protease resistant proteins in the diabetic rat kidney
- PMID: 23118466
- PMCID: PMC3536903
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M112.020651
Proteomic analysis of protease resistant proteins in the diabetic rat kidney
Abstract
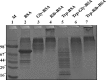
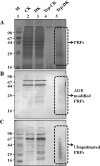
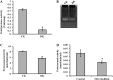
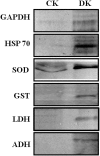
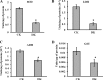
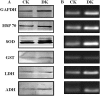
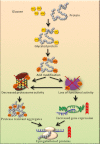
Glycation induced protein aggregation has been implicated in the development of diabetic complications and neurodegenerative diseases. These aggregates are known to be resistant to proteolytic digestion. Here we report the identification of protease resistant proteins from the streptozotocin induced diabetic rat kidney, which included enzymes in glucose metabolism and stress response proteins. These protease resistant proteins were characterized to be advanced glycation end products modified and ubiquitinated by immunological and mass spectrometry analysis. Further, diabetic rat kidney exhibited significantly impaired proteasomal activity. The functional analysis of identified physiologically important enzymes showed that their activity was reduced in diabetic condition. Loss of functional activity of these proteins was compensated by enhanced gene expression. Aggregation prone regions were predicted by in silico analysis and compared with advanced glycation end products modification sites. These findings suggested that the accumulation of protein aggregates is an inevitable consequence of impaired proteasomal activity and protease resistance due to advanced glycation end products modification.
Figures

References
-
- Brownlee M. (2001) Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 414, 813–820 - PubMed
-
- Peppa M., Uribarri J., Vlassara H. (2003) Glucose, Advanced Glycation End products, and Diabetes complications: What is new and what works. Clin. Diabetes. 21, 186–187
-
- Bulteau A. L., Verbeke P., Petropoulos I., Chaffotte A. F., Friguet B. (2001) Proteasome inhibition in glyoxal-treated fibroblasts and resistance of glycated glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase to 20s proteasome degradation in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 45662–45668 - PubMed
-
- Reddy G. K., Stehno-Bittel L., Enwemeka C. S. (2002) Glycation-induced matrix stability in the rabbit achilles tendon. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 399, 174–180 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

