Chronic medical conditions and risk of sepsis
- PMID: 23118977
- PMCID: PMC3485139
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048307
Chronic medical conditions and risk of sepsis
Abstract
Background: We sought to determine the associations between baseline chronic medical conditions and future risk of sepsis.
Methods: Longitudinal cohort study using the 30,239 community-dwelling participants of the REGARDS cohort. We determined associations between baseline chronic medical conditions and incident sepsis episodes, defined as hospitalization for an infection with the presence of infection plus two or more systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria.
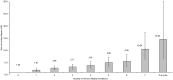
Results: Over the mean observation time of 4.6 years (February 5, 2003 through October 14, 2011), there were 975 incident cases of sepsis. Incident sepsis episodes were associated with older age (p<0.001), white race (HR 1.39; 95% CI: 1.22-1.59), lower education (p<0.001) and income (p<0.001), tobacco use (p<0.001), and alcohol use (p = 0.02). Incident sepsis episodes were associated with baseline chronic lung disease (adjusted HR 2.43; 95% CI: 2.05-2.86), peripheral artery disease (2.16; 1.58-2.95), chronic kidney disease (1.99; 1.73-2.29), myocardial infarction 1.79 (1.49-2.15), diabetes 1.78 (1.53-2.07), stroke 1.67 (1.34-2.07), deep vein thrombosis 1.63 (1.29-2.06), coronary artery disease 1.61 (1.38-1.87), hypertension 1.49 (1.29-1.74), atrial fibrillation 1.48 (1.21-1.81) and dyslipidemia 1.16 (1.01-1.34). Sepsis risk increased with the number of chronic medical conditions (p<0.001).
Conclusions: Individuals with chronic medical conditions are at increased risk of future sepsis events.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E, Angus D, et al. (2003) 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Intensive Care Med 29: 530–538. - PubMed
-
- Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, et al. (2001) Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med 29: 1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Wang HE, Shapiro NI, Angus DC, Yealy DM (2007) National estimates of severe sepsis in United States emergency departments. Crit Care Med 35: 1928–1936. - PubMed
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M (2003) The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med 348: 1546–1554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

