Cholesterol: its regulation and role in central nervous system disorders
- PMID: 23119149
- PMCID: PMC3483652
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/292598
Cholesterol: its regulation and role in central nervous system disorders
Abstract
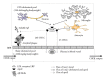
Cholesterol is a major constituent of the human brain, and the brain is the most cholesterol-rich organ. Numerous lipoprotein receptors and apolipoproteins are expressed in the brain. Cholesterol is tightly regulated between the major brain cells and is essential for normal brain development. The metabolism of brain cholesterol differs markedly from that of other tissues. Brain cholesterol is primarily derived by de novo synthesis and the blood brain barrier prevents the uptake of lipoprotein cholesterol from the circulation. Defects in cholesterol metabolism lead to structural and functional central nervous system diseases such as Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome, Niemann-Pick type C disease, and Alzheimer's disease. These diseases affect different metabolic pathways (cholesterol biosynthesis, lipid transport and lipoprotein assembly, apolipoproteins, lipoprotein receptors, and signaling molecules). We review the metabolic pathways of cholesterol in the CNS and its cell-specific and microdomain-specific interaction with other pathways such as the amyloid precursor protein and discuss potential treatment strategies as well as the effects of the widespread use of LDL cholesterol-lowering drugs on brain functions.
Figures
References
-
- Dietschy JM, Turley SD. Cholesterol metabolism in the brain. Current Opinion in Lipidology. 2001;12(2):105–112. - PubMed
-
- Björkhem I, Meaney S, Fogelman AM. Brain cholesterol: long secret life behind a barrier. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2004;24(5):806–815. - PubMed
-
- Fester L, Zhou L, Bütow A, et al. Cholesterol-promoted synaptogenesis requires the conversion of cholesterol to estradiol in the hippocampus. Hippocampus. 2009;19(8):692–705. - PubMed
-
- Goritz C, Mauch DH, Pfrieger FW. Multiple mechanisms mediate cholesterol-induced synaptogenesis in a CNS neuron. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience. 2005;29(2):190–201. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

