The impact of oral health literacy on periodontal health status
- PMID: 23121152
- PMCID: PMC3800213
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1752-7325.2012.00375.x
The impact of oral health literacy on periodontal health status
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to describe oral health literacy (OHL) among periodontal patients and to examine its association with periodontal health status.
Methods: This cross-sectional study included new and referred patients presenting to the University of North Carolina Graduate Periodontology Clinic. Sociodemographic and dental history information were collected. OHL was measured using a dental word recognition instrument, Rapid Estimate of Adult Literacy-30 (REALD-30). Clinical periodontal examinations were completed.
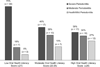
Results: One hundred and twenty-eight participants enrolled and 121 completed all study examinations and instruments. Despite a high level of education among participants in our study, low levels of OHL were found in one-third (33 percent) of the study population. Thirty-one percent had moderate OHL (score of 22-25), 37 percent had high OHL (score ≥ 26). The mean REALD-30 score was 23. Fifty-three percent of participants had severe periodontitis, 29 percent had moderate periodontitis, and 18 percent had mild or no periodontitis. Bivariate analysis showed a significant association between OHL and periodontal status (P < 0.05). The effect of OHL on periodontal health status remained statistically significant (P < 0.002) even after controlling for smoking, race, and dental insurance.
Conclusion: Lower OHL was associated with more severe periodontal disease among new and referred patients presenting to the University of North Carolina Graduate Periodontology Clinics.
Keywords: health literacy; literacy; oral health; periodontal disease; periodontitis.
© 2012 American Association of Public Health Dentistry.
Figures
References
-
- Kutner M, Greenberg E, Baer J. The health literacy of America’s adults: results from the 2003 National Assessment of Adult Literacy. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics; 2006.
-
- Schillinger D, Grumbach K, Piette J, Wang F, Osmond D, Daher C, Palacios J, Sullivan GD, Bindman AB. Association of health literacy with diabetes outcomes. JAMA. 2002;288(4):475–482. - PubMed
-
- Villaire M, Mayer G. Low health literacy: the impact on chronic illness management. Prof Case Manag. 2007;12(4):213–216. quiz 7–8. - PubMed
-
- National institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research, National Institute of Health, U.S. Public Health Service, Department of Health Human Services. The invisible barrier: literacy and its relationship with oral health. A report of a workgroup sponsored by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research, National Institute of Health, U.S. Public Health Service, Department of Health and Human Services. J Public Health Dent. 2005;65(3):174–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical