Neutral solution low in glucose degradation products is associated with less peritoneal fibrosis and vascular sclerosis in patients receiving peritoneal dialysis
- PMID: 23123670
- PMCID: PMC3649892
- DOI: 10.3747/pdi.2011.00270
Neutral solution low in glucose degradation products is associated with less peritoneal fibrosis and vascular sclerosis in patients receiving peritoneal dialysis
Abstract
Background: The effects of novel biocompatible peritoneal dialysis (PD) solutions on human peritoneal membrane pathology have yet to be determined. Quantitative evaluation of human peritoneal biopsy specimens may reveal the effects of the new solutions on peritoneal membrane pathology. ♢
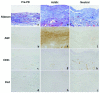
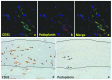
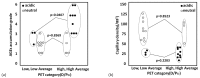
Methods: Peritoneal specimens from 24 PD patients being treated with either acidic solution containing high-glucose degradation products [GDPs (n = 12)] or neutral solution with low GDPs (n = 12) were investigated at the end of PD. As controls, pre-PD peritoneal specimens, obtained from 13 patients at PD catheter insertion, were also investigated. The extent of peritoneal fibrosis, vascular sclerosis, and advanced glycation end-product (AGE) accumulation were evaluated by quantitative or semi-quantitative methods. The average densities of CD31-positive vessels and podoplanin-positive lymphatic vessels were also determined. ♢
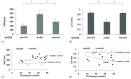
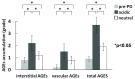
Results: Peritoneal membrane fibrosis, vascular sclerosis, and AGE accumulation were significantly suppressed in the neutral group compared with the acidic group. The neutral group also showed lower peritoneal equilibration test scores and preserved ultrafiltration volume. The density of blood capillaries, but not of lymphatic capillaries, was significantly increased in the neutral group compared with the acidic and pre-PD groups. ♢
Conclusions: Neutral solutions with low GDPs are associated with less peritoneal membrane fibrosis and vascular sclerosis through suppression of AGE accumulation. However, contrary to expectation, blood capillary density was increased in the neutral group. The altered contents of the new PD solutions modified peritoneal membrane morphology and function in patients undergoing PD.
Keywords: AGEs; GDPs; angiogenesis; biocompatible solution; peritoneal fibrosis; vascular sclerosis.
Figures

References
-
- Jörres A, Bender TO, Finn A, Witowski J, Fröhlich S, Gahl GM, et al. Biocompatibility and buffers: effect of bicarbonate-buffered peritoneal dialysis fluids on peritoneal cell function. Kidney Int 1998; 54:2184–93 - PubMed
-
- Jörres A, Witowski J. Lessons from basic research for PD treatment. Perit Dial Int 2005; 25(Suppl 3):S35–8 - PubMed
-
- Topley N, Kaur D, Petersen MM, Jörres A, Williams JD, Faict D, et al. In vitro effects of bicarbonate and bicarbonate-lactate buffered peritoneal dialysis solutions on mesothelial and neutrophil function. J Am Soc Nephrol 1996; 7:218–24 - PubMed
-
- Combet S, Miyata T, Moulin P, Pouthier D, Goffin E, Devuyst O. Vascular proliferation and enhanced expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in human peritoneum exposed to long-term peritoneal dialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2000; 11:717–28 - PubMed
-
- Pecoits-Filho R, Araújo MR, Lindholm B, Stenvinkel P, Abensur H, Romão JE, Jr, et al. Plasma and dialysate IL-6 and VEGF concentrations are associated with high peritoneal solute transport rate. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2002; 17:1480–6 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

