The human W42R γD-crystallin mutant structure provides a link between congenital and age-related cataracts
- PMID: 23124202
- PMCID: PMC3537076
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.416354
The human W42R γD-crystallin mutant structure provides a link between congenital and age-related cataracts
Abstract
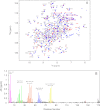
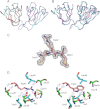
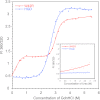
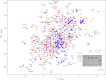
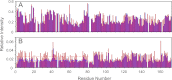
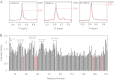
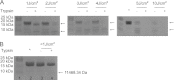
Some mutants of human γD-crystallin are closely linked to congenital cataracts, although the detailed molecular mechanisms of mutant-associated cataract formation are generally not known. Here we report on a recently discovered γD-crystallin mutant (W42R) that has been linked to autosomal dominant, congenital cataracts in a Chinese family. The mutant protein is much less soluble and stable than wild-type γD-crystallin. We solved the crystal structure of W42R at 1.7 Å resolution, which revealed only minor differences from the wild-type structure. Interestingly, the W42R variant is highly susceptible to protease digestion, suggesting the presence of a small population of partially unfolded protein. This partially unfolded species was confirmed and quantified by NMR spectroscopy. Hydrogen/deuterium exchange experiments revealed chemical exchange between the folded and unfolded species. Exposure of wild-type γD-crystallin to UV caused damage to the N-terminal domain of the protein, resulting in very similar proteolytic susceptibility as observed for the W42R mutant. Altogether, our combined data allowed us to propose a model for W42R pathogenesis, with the W42R mutant serving as a mimic for photodamaged γD-crystallin involved in age-related cataract.
Figures

References
-
- Reddy M. A., Bateman O. A., Chakarova C., Ferris J., Berry V., Lomas E., Sarra R., Smith M. A., Moore A. T., Bhattacharya S. S., Slingsby C. (2004) Characterization of the G91del CRYBA1/3-crystallin protein: a cause of human inherited cataract. Hum. Mol. Genet. 13, 945–953 - PubMed
-
- Vijaya R., Gupta R., Panda G., Ravishankar K., Kumaramanickavel G. (1997) Genetic analysis of adult-onset cataract in a city-based ophthalmic hospital. Clin. Genet. 52, 427–431 - PubMed
-
- Rahi J. S., Dezateux C. (2000) Congenital and infantile cataract in the United Kingdom: underlying or associated factors. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 41, 2108–2114 - PubMed
-
- Lampi K. J., Ma Z., Shih M., Shearer T. R., Smith J. B., Smith D. L., David L. L. (1997) Sequence analysis of βA3, βB3, and βA4 crystallins completes the identification of the major proteins in young human lens. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 2268–2275 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

