Association of physical activity with survival among ambulatory patients on dialysis: the Comprehensive Dialysis Study
- PMID: 23124787
- PMCID: PMC3562868
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.08560812
Association of physical activity with survival among ambulatory patients on dialysis: the Comprehensive Dialysis Study
Abstract
Background and objectives: Despite high mortality and low levels of physical activity (PA) among patients starting dialysis, the link between low PA and mortality has not been carefully evaluated.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: The Comprehensive Dialysis Study was a prospective cohort study that enrolled patients who started dialysis between June 2005 and June 2007 in a random sample of dialysis facilities in the United States. The Human Activity Profile (HAP) was administered to estimate PA among 1554 ambulatory enrolled patients in the Comprehensive Dialysis Study. Patients were followed until death or September 30, 2009, and the major outcome was all-cause mortality.
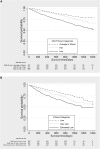
Results: The average age was 59.8 (14.2) years; 55% of participants were male, 28% were black, and 56% had diabetes mellitus. The majority (57.3%) had low fitness estimated from the HAP score. The median follow-up was 2.6 (interquartile range, 2.2-3.1) years. The association between PA and mortality was linear across the range of scores (1-94). After multivariable adjustment, lower adjusted activity score on the HAP was associated with higher mortality (hazard ratio, 1.30; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-1.39 per 10 points). Patients in the lowest level of fitness experienced a 3.5-fold (95% confidence interval, 2.54-4.89) increase in risk of death compared with those with average or above fitness.
Conclusions: Low levels of PA are strongly associated with mortality among patients new to dialysis. Interventions aimed to preserve or enhance PA should be prospectively tested.
Figures
References
-
- de Jager DJ, Grootendorst DC, Jager KJ, van Dijk PC, Tomas LM, Ansell D, Collart F, Finne P, Heaf JG, De Meester J, Wetzels JFM, Rosendaal FR, Dekker FW: Cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality among patients starting dialysis. JAMA 302: 1782–1789, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Johansen KL, Chertow GM, Ng AV, Mulligan K, Carey S, Schoenfeld PY, Kent-Braun JA: Physical activity levels in patients on hemodialysis and healthy sedentary controls. Kidney Int 57: 2564–2570, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Cupisti A, Capitanini A, Betti G, D’Alessandro C, Barsotti G: Assessment of habitual physical activity and energy expenditure in dialysis patients and relationships to nutritional parameters. Clin Nephrol 75: 218–225, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Baria F, Kamimura MA, Avesani CM, Lindholm B, Stenvinkel P, Draibe SA, Cuppari L: Activity-related energy expenditure of patients undergoing hemodialysis. J Ren Nutr 21: 226–234, 2011 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

