CD73-generated adenosine: orchestrating the tumor-stroma interplay to promote cancer growth
- PMID: 23125525
- PMCID: PMC3482007
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/485156
CD73-generated adenosine: orchestrating the tumor-stroma interplay to promote cancer growth
Abstract
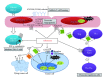
Despite the coming of age of cancer immunotherapy, clinical benefits are still modest. An important barrier to successful cancer immunotherapy is that tumors employ a number of mechanisms to facilitate immune escape, including the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, the recruitment of regulatory immune subsets, and the production of immunosuppressive metabolites. Significant therapeutic opportunity exists in targeting these immunosuppressive pathways. One such immunosuppressive pathway is the production of extracellular adenosine by CD73, an ectonucleotidase overexpressed in various types of cancer. We hereafter review the biology of CD73 and its role in cancer progression and metastasis. We describe the role of extracellular adenosine in promoting tumor growth through paracrine and autocrine action on tumor cells, endothelial cells, and immune cells.
Figures
References
-
- Mlecnik B, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, et al. Histopathologic-based prognostic factors of colorectal cancers are associated with the state of the local immune reaction. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2011;29(6):610–618. - PubMed
-
- Galluzzi L, Senovilla L, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G. The secret ally: immunostimulation by anticancer drugs. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2012;11(3):215–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

