The Multi-Leu peptide inhibitor discriminates between PACE4 and furin and exhibits antiproliferative effects on prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 23126600
- PMCID: PMC3523546
- DOI: 10.1021/jm3011178
The Multi-Leu peptide inhibitor discriminates between PACE4 and furin and exhibits antiproliferative effects on prostate cancer cells
Abstract
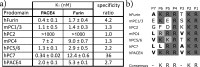
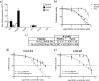
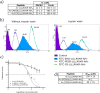
The proprotein convertases (PCs) play an important role in protein precursor activation through processing at paired basic residues. However, significant substrate cleavage redundancy has been reported between PCs. The question remains whether specific PC inhibitors can be designed. This study describes the identification of the sequence LLLLRVKR, named Multi-Leu (ML)-peptide, that displayed a 20-fold selectivity on PACE4 over furin, two enzymes with similar structural characteristics. We have previously demonstrated that PACE4 plays an important role in prostate cancer and could be a druggable target. The present study demonstrates that the ML-peptide significantly reduced the proliferation of DU145 and LNCaP prostate cancer-derived cell lines and induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. However, the ML-peptide must enter the cell to inhibit proliferation. It is concluded that peptide-based inhibitors can yield specific PC inhibitors and that the ML-peptide is an important lead compound that could potentially have applications in prostate cancer.
Figures




References
-
- Seidah N. G.; Mayer G.; Zaid A.; Rousselet E.; Nassoury N.; Poirier S.; Essalmani R.; Prat A. The activation and physiological functions of the proprotein convertases. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40(6–7), 1111–1125. - PubMed
-
- Mayer G.; Hamelin J.; Asselin M. C.; Pasquato A.; Marcinkiewicz E.; Tang M.; Tabibzadeh S.; Seidah N. G. The regulated cell surface zymogen activation of the proprotein convertase PC5A directs the processing of its secretory substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283(4), 2373–2384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

