Mouse mtDNA mutant model of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy
- PMID: 23129651
- PMCID: PMC3523873
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1217113109
Mouse mtDNA mutant model of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy
Abstract
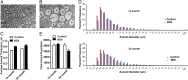
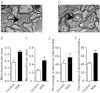
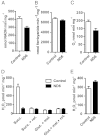
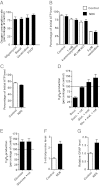
An animal model of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) was produced by introducing the human optic atrophy mtDNA ND6 P25L mutation into the mouse. Mice with this mutation exhibited reduction in retinal function by elecroretinogram (ERG), age-related decline in central smaller caliber optic nerve fibers with sparing of larger peripheral fibers, neuronal accumulation of abnormal mitochondria, axonal swelling, and demyelination. Mitochondrial analysis revealed partial complex I and respiration defects and increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, whereas synaptosome analysis revealed decreased complex I activity and increased ROS but no diminution of ATP production. Thus, LHON pathophysiology may result from oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Leber hereditary optic neuropathy and oxidative stress.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Dec 4;109(49):19882-3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218953109. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23197830 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wallace DC, et al. Mitochondrial DNA mutation associated with Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy. Science. 1988;242(4884):1427–1430. - PubMed
-
- Sadun AA, La Morgia C, Carelli V. Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2011;13(1):109–117. - PubMed
-
- Johns DR, Neufeld MJ, Park RD. An ND-6 mitochondrial DNA mutation associated with Leber hereditary optic neuropathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992;187(3):1551–1557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

