Most rhesus macaques infected with the CCR5-tropic SHIV(AD8) generate cross-reactive antibodies that neutralize multiple HIV-1 strains
- PMID: 23129652
- PMCID: PMC3511737
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1217443109
Most rhesus macaques infected with the CCR5-tropic SHIV(AD8) generate cross-reactive antibodies that neutralize multiple HIV-1 strains
Abstract
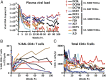
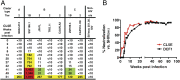
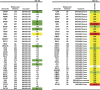
The induction of broadly reacting neutralizing antibodies has been a major goal of HIV vaccine research. Characterization of a pathogenic CCR5 (R5)-tropic SIV/HIV chimeric virus (SHIV) molecular clone (SHIV(AD8-EO)) revealed that eight of eight infected animals developed cross-reactive neutralizing antibodies (NAbs) directed against an envelope glycoprotein derived from the heterologous HIV-1(DH12) strain. A panel of plasmas, collected from monkeys inoculated with either molecularly cloned or uncloned SHIV(AD8) stocks, exhibited cross-neutralization against multiple tier 1 and tier 2 HIV-1 clade B isolates. One SHIV(AD8)-infected animal also developed NAbs against clades A and C HIV-1 strains. In this particular infected macaque, the cross-reacting anti-HIV-1 NAbs produced between weeks 7 and 13 were directed against a neutralization-sensitive virus strain, whereas neutralizing activities emerging at weeks 41-51 targeted more neutralization-resistant HIV-1 isolates. These results indicate that the SHIV(AD8) macaque model represents a potentially valuable experimental system for investigating B-cell maturation and the induction of cross-reactive NAbs directed against multiple HIV-1 strains.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

