HIV incidence determination in the United States: a multiassay approach
- PMID: 23129760
- PMCID: PMC3532826
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jis659
HIV incidence determination in the United States: a multiassay approach
Abstract
Background: Accurate testing algorithms are needed for estimating human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) incidence from cross-sectional surveys.
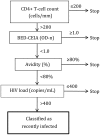
Methods: We developed a multiassay algorithm (MAA) for HIV incidence that includes the BED capture enzyme immunoassay (BED-CEIA), an antibody avidity assay, HIV load, and CD4(+) T-cell count. We analyzed 1782 samples from 709 individuals in the United States who had a known duration of HIV infection (range, 0 to >8 years). Logistic regression with cubic splines was used to compare the performance of the MAA to the BED-CEIA and to determine the window period of the MAA. We compared the annual incidence estimated with the MAA to the annual incidence based on HIV seroconversion in a longitudinal cohort.
Results: The MAA had a window period of 141 days (95% confidence interval [CI], 94-150) and a very low false-recent misclassification rate (only 0.4% of 1474 samples from subjects infected for >1 year were misclassified as indicative of recent infection). In a cohort study, annual incidence based on HIV seroconversion was 1.04% (95% CI, .70%-1.55%). The incidence estimate obtained using the MAA was essentially identical: 0.97% (95% CI, .51%-1.71%).
Conclusions: The MAA is as sensitive for detecting recent HIV infection as the BED-CEIA and has a very low rate of false-recent misclassification. It provides a powerful tool for cross-sectional HIV incidence determination.
Figures

Comment in
-
Determining HIV incidence in populations: moving in the right direction.J Infect Dis. 2013 Jan 15;207(2):204-6. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis661. Epub 2012 Nov 5. J Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23129757 No abstract available.
References
-
- Brookmeyer R. Measuring the HIV/AIDS epidemic: approaches and challenges. Epidemiol Rev. 2010;32:26–37. - PubMed
-
- UNAIDS. Geneva, Switzerland: UNAIDS; 2010. Global report: UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic 2010.
-
- Brookmeyer R, Quinn T, Shepherd M, Mehendale S, Rodrigues J, Bollinger R. The AIDS epidemic in India: a new method for estimating current human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) incidence rates. Am J Epidemiol. 1995;142:709–13. - PubMed
-
- Brookmeyer R, Quinn TC. Estimation of current human immunodeficiency virus incidence rates from a cross-sectional survey using early diagnostic tests. Am J Epidemiol. 1995;141:166–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI-45202/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI35043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI095068/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA12568/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI35041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA-04334/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA036297/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AI35176/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI045200/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI35040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA004334/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI048054/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI48054/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI46745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI095068/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI35042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI35039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012568/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1-AI068613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI046745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

