Application of percutaneous cardiopulmonary support for cardiac tamponade following blunt chest trauma: two case reports
- PMID: 23130310
- PMCID: PMC3487020
- DOI: 10.5090/kjtcs.2012.45.5.334
Application of percutaneous cardiopulmonary support for cardiac tamponade following blunt chest trauma: two case reports
Abstract
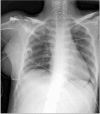
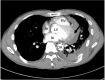
Since the advent of percutaneous cardiopulmonary support (PCPS), its application has been extended to massively injured patient. Cardiac injury following blunt chest trauma brings out high mortality and morbidity. In our cases, patients had high injury severity score by blunt trauma and presented sudden hemodynamic collapse in emergency room. We quickly detected cardiac tamponade by focused assessment with sonography for trauma and implemented PCPS. As PCPS established, their vital sign restored and then, they were transferred to the operation room (OR) securely. After all injured lesion repaired, PCPS weaned successfully in OR. They were discharged without complication on day 26 and 55, retrospectively.
Keywords: Cardiac rupture; Cardiac tamponade; Extracorporeal circulation; Trauma, blunt; Ultrasonic diagnosis.
Figures
References
-
- Karmy-Jones R, Jurkovich GJ. Blunt chest trauma. Curr Probl Surg. 2004;41:211–380. - PubMed
-
- Krasna MJ, Flancbaum L. Blunt cardiac trauma: clinical manifestations and management. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1992;4:195–202. - PubMed
-
- Perchinsky MJ, Long WB, Hill JG, Parsons JA, Bennett JB. Extracorporealcardiopulmonary life support with heparin-bonded circuitry in the resuscitation of massively injured trauma patients. Am J Surg. 1995;169:488–491. - PubMed
-
- Thiagarajan RR, Brogan TV, Scheurer MA, Laussen PC, Rycus PT, Bratton SL. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation to support cardiopulmonary resuscitation inadults. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;87:778–785. - PubMed
-
- Grande AM, Rinaldi M, Pasquino S, Dore R, Vigano M. Nonpenetrating rightatrial and pericardial trauma. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;76:923–925. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials