Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for XIAP deficiency: an international survey reveals poor outcomes
- PMID: 23131490
- PMCID: PMC5162550
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-06-432500
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for XIAP deficiency: an international survey reveals poor outcomes
Abstract
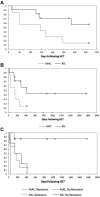
There have been no studies on patient outcome after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) in patients with X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) deficiency. To estimate the success of HCT, we conducted an international survey of transplantation outcomes. Data were reported for 19 patients. Seven patients received busulfan-containing myeloablative conditioning (MAC) regimens. Eleven patients underwent reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) regimens predominantly consisting of alemtuzumab, fludarabine, and melphalan. One patient received an intermediate-intensity regimen. Survival was poor in the MAC group, with only 1 patient surviving (14%). Most deaths were from transplantation-related toxicities, including venoocclusive disease and pulmonary hemorrhage. Of the 11 patients who received RIC, 6 are currently surviving at a median of 570 days after HCT (55%). Preparative regimen and HLH activity affected outcomes, and of RIC patients reported to be in remission from HLH, survival is 86% (P = .03). We conclude that MAC regimens should not be used for patients with XIAP deficiency. It is possible that the loss of XIAP and its antiapoptotic functions contributes to the high incidence of toxicities observed with MAC regimens. RIC regimens should be pursued with caution and, if possible, efforts should be made to ensure HLH remission before HCT in these patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduced-intensity conditioning hematopoietic cell transplantation is an effective treatment for patients with SLAM-associated protein deficiency/X-linked lymphoproliferative disease type 1.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014 Oct;20(10):1641-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2014.06.003. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014. PMID: 24923536
-
Haploidentical Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for XIAP Deficiency: a Single-Center Report.J Clin Immunol. 2020 Aug;40(6):893-900. doi: 10.1007/s10875-020-00795-6. Epub 2020 Jul 5. J Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32627096
-
Reduced-intensity conditioning significantly improves survival of patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation.Blood. 2010 Dec 23;116(26):5824-31. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-04-282392. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20855862
-
An International Survey of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia.J Clin Immunol. 2023 Nov;43(8):1827-1839. doi: 10.1007/s10875-023-01551-2. Epub 2023 Jul 16. J Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37454339 Review.
-
Successful stem cell transplant with antibody-based conditioning for XIAP deficiency with refractory hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.Blood. 2013 Jun 13;121(24):4966-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-01-478735. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23766462 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Very Early-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Challenging Field for Pediatric Gastroenterologists.Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2020 Sep;23(5):411-422. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2020.23.5.411. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32953636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disorders of ubiquitylation: unchained inflammation.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022 Aug;18(8):435-447. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00778-4. Epub 2022 May 6. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35523963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Successful outcome following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adults with primary immunodeficiency.Blood. 2018 Feb 22;131(8):917-931. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-09-807487. Epub 2017 Dec 26. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29279357 Free PMC article.
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for primary immunodeficiencies.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2014 Dec;28(6):1157-70. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2014. PMID: 25459185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TNFR2 induced priming of the inflammasome leads to a RIPK1-dependent cell death in the absence of XIAP.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Sep 20;10(10):700. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1938-x. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31541082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henter JI, Samuelsson-Horne A, Arico M, et al. Treatment of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with HLH-94 immunochemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 2002;100(7):2367–2373. - PubMed
-
- Horne A, Janka G, Maarten Egeler R, et al. Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation in haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Br J Haematol. 2005;129(5):622–630. - PubMed
-
- Ouachée-Chardin M, Elie C, de Saint Basile G, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a single-center report of 48 patients. Pediatrics. 2006;117(4):e743–750. - PubMed
-
- Baker KS, Filipovich AH, Gross TG, et al. Unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008;42(3):175–180. - PubMed
-
- Cesaro S, Locatelli F, Lanino E, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a retrospective analysis of data from the Italian Association of Pediatric Hematology Oncology (AIEOP). Haematologica. 2008;93(11):1694–1701. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources