Developmental origin of patchy axonal connectivity in the neocortex: a computational model
- PMID: 23131803
- PMCID: PMC3888370
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhs327
Developmental origin of patchy axonal connectivity in the neocortex: a computational model
Abstract
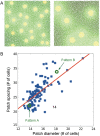
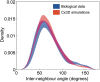
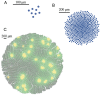
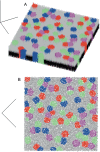
Injections of neural tracers into many mammalian neocortical areas reveal a common patchy motif of clustered axonal projections. We studied in simulation a mathematical model for neuronal development in order to investigate how this patchy connectivity could arise in layer II/III of the neocortex. In our model, individual neurons of this layer expressed the activator-inhibitor components of a Gierer-Meinhardt reaction-diffusion system. The resultant steady-state reaction-diffusion pattern across the neuronal population was approximately hexagonal. Growth cones at the tips of extending axons used the various morphogens secreted by intrapatch neurons as guidance cues to direct their growth and invoke axonal arborization, so yielding a patchy distribution of arborization across the entire layer II/III. We found that adjustment of a single parameter yields the intriguing linear relationship between average patch diameter and interpatch spacing that has been observed experimentally over many cortical areas and species. We conclude that a simple Gierer-Meinhardt system expressed by the neurons of the developing neocortex is sufficient to explain the patterns of clustered connectivity observed experimentally.
Keywords: neural development; reaction–diffusion models; self-organization; simulation; superficial patch system.
Figures




Similar articles
-
From neural arbors to daisies.Cereb Cortex. 2011 May;21(5):1118-33. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhq184. Epub 2010 Sep 30. Cereb Cortex. 2011. PMID: 20884721 Free PMC article.
-
Axonal surface molecules act in combination with semaphorin 3a during the establishment of corticothalamic projections.Cereb Cortex. 2001 Mar;11(3):278-85. doi: 10.1093/cercor/11.3.278. Cereb Cortex. 2001. PMID: 11230099
-
Developing neocortex organization and connectivity in cats revealed by direct correlation of diffusion tractography and histology.Cereb Cortex. 2011 Jan;21(1):200-11. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhq084. Epub 2010 May 21. Cereb Cortex. 2011. PMID: 20494968 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal circuits of the neocortex.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2004;27:419-51. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.27.070203.144152. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15217339 Review.
-
A modeler's view on the spatial structure of intrinsic horizontal connectivity in the neocortex.Prog Neurobiol. 2010 Nov;92(3):277-92. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.05.001. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Prog Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20685378 Review.
Cited by
-
Developmental self-construction and -configuration of functional neocortical neuronal networks.PLoS Comput Biol. 2014 Dec 4;10(12):e1003994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003994. eCollection 2014 Dec. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014. PMID: 25474693 Free PMC article.
-
Unification of free energy minimization, spatiotemporal energy, and dimension reduction models of V1 organization: Postnatal learning on an antenatal scaffold.Front Comput Neurosci. 2022 Oct 14;16:869268. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2022.869268. eCollection 2022. Front Comput Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36313813 Free PMC article.
-
Calibration of stochastic, agent-based neuron growth models with approximate Bayesian computation.J Math Biol. 2024 Oct 8;89(5):50. doi: 10.1007/s00285-024-02144-2. J Math Biol. 2024. PMID: 39379537 Free PMC article.
-
Modular Organization of Signal Transmission in Primate Somatosensory Cortex.Front Neuroanat. 2022 Jul 8;16:915238. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2022.915238. eCollection 2022. Front Neuroanat. 2022. PMID: 35873660 Free PMC article.
-
A proto-architecture for innate directionally selective visual maps.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 23;9(7):e102908. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102908. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25054209 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angelucci A, Sainsbury K. Contribution of feedforward thalamic afferents and corticogeniculate feedback to the spatial summation area of macaque V1 and LGN. J Comp Neurol. 2006;498:330–351. - PubMed
-
- Binzegger T, Douglas R, Martin K. An axonal perspective on cortical circuits. In: Feldmeyer D, Lübke JHR, editors. New aspects of axonal structure and function. New York (NY): Springer; 2010. pp. 117–139.
-
- Bonabeau E. From classical models of morphogenesis to agent-based models of pattern formation. Artif Life. 1997;3:191–211. - PubMed

