Cryptococcus neoformans requires the ESCRT protein Vps23 for iron acquisition from heme, for capsule formation, and for virulence
- PMID: 23132495
- PMCID: PMC3536123
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01037-12
Cryptococcus neoformans requires the ESCRT protein Vps23 for iron acquisition from heme, for capsule formation, and for virulence
Abstract
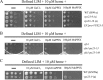
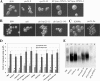
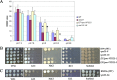
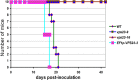
Iron availability is a key regulator of virulence factor elaboration in Cryptococcus neoformans, the causative agent of fungal meningoencephalitis in HIV/AIDS patients. In addition, iron is an essential nutrient for pathogen proliferation in mammalian hosts but little is known about the mechanisms of iron sensing and uptake in fungal pathogens that attack humans. In this study, we mutagenized C. neoformans by Agrobacterium-mediated T-DNA insertion and screened for mutants with reduced growth on heme as the sole iron source. Among 34 mutants, we identified a subset with insertions in the gene for the ESCRT-I (endosomal sorting complex required for transport) protein Vps23 that resulted in a growth defect on heme, presumably due to a defect in uptake via endocytosis or misregulation of iron acquisition from heme. Remarkably, vps23 mutants were also defective in the elaboration of the cell-associated capsular polysaccharide that is a major virulence factor, while overexpression of Vps23 resulted in cells with a slightly enlarged capsule. These phenotypes were mirrored by a virulence defect in the vps23 mutant in a mouse model of cryptococcosis and by hypervirulence of the overexpression strain. Overall, these results reveal an important role for trafficking via ESCRT functions in both heme uptake and capsule formation, and they further reinforce the connection between iron and virulence factor deployment in C. neoformans.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The endosomal sorting complex required for transport machinery influences haem uptake and capsule elaboration in Cryptococcus neoformans.Mol Microbiol. 2015 Jun;96(5):973-92. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12985. Epub 2015 Mar 28. Mol Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25732100 Free PMC article.
-
The Monothiol Glutaredoxin Grx4 Regulates Iron Homeostasis and Virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans.mBio. 2018 Dec 4;9(6):e02377-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02377-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30514787 Free PMC article.
-
Iron and fungal pathogenesis: a case study with Cryptococcus neoformans.Cell Microbiol. 2008 Feb;10(2):277-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.01077.x. Epub 2007 Nov 27. Cell Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18042257 Review.
-
The Novel J-Domain Protein Mrj1 Is Required for Mitochondrial Respiration and Virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans.mBio. 2020 Jun 9;11(3):e01127-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01127-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32518190 Free PMC article.
-
An encapsulation of iron homeostasis and virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans.Trends Microbiol. 2013 Sep;21(9):457-65. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2013.05.007. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Trends Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23810126 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of the putative Rab GTPase, Ypt7, impairs the virulence of Cryptococcus neoformans.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jul 25;15:1437579. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1437579. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39119141 Free PMC article.
-
Role of clathrin-mediated endocytosis in the use of heme and hemoglobin by the fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans.Cell Microbiol. 2019 Mar;21(3):e12961. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12961. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Cell Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30291809 Free PMC article.
-
The Sec1/Munc18 (SM) protein Vps45 is involved in iron uptake, mitochondrial function and virulence in the pathogenic fungus Cryptococcus neoformans.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Aug 2;14(8):e1007220. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007220. eCollection 2018 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 30071112 Free PMC article.
-
EhVps23: A Component of ESCRT-I That Participates in Vesicular Trafficking and Phagocytosis of Entamoeba histolytica.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Oct 29;11:770759. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.770759. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34778112 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay between electron transport chain function and iron regulatory factors influences melanin formation in Cryptococcus neoformans.mSphere. 2024 May 29;9(5):e0025024. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00250-24. Epub 2024 Apr 30. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 38687055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Park BJ, Wannemuehler KA, Marston BJ, Govender N, Pappas PG, Chiller TM. 2009. Estimation of the current global burden of cryptococcal meningitis among persons living with HIV/AIDS. AIDS 23:525–530 - PubMed
-
- Jacobson ES, Compton GM. 1996. Discordant regulation of phenoloxidase and capsular polysaccharide in Cryptococcus neoformans. J. Med. Vet. Mycol. 34:289–291 - PubMed
-
- Jung WH, Kronstad JW. 2008. Iron and fungal pathogenesis: a case study with Cryptococcus neoformans. Cell. Microbiol. 10:277–284 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

