Impact of the CYP4F2 p.V433M polymorphism on coumarin dose requirement: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 23132553
- PMCID: PMC3731755
- DOI: 10.1038/clpt.2012.184
Impact of the CYP4F2 p.V433M polymorphism on coumarin dose requirement: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
A systematic review and a meta-analysis were performed to quantify the accumulated information from genetic association studies investigating the impact of the CYP4F2 rs2108622 (p.V433M) polymorphism on coumarin dose requirement. An additional aim was to explore the contribution of the CYP4F2 variant in comparison with, as well as after stratification for, the VKORC1 and CYP2C9 variants. Thirty studies involving 9,470 participants met prespecified inclusion criteria. As compared with CC-homozygotes, T-allele carriers required an 8.3% (95% confidence interval (CI): 5.6-11.1%; P < 0.0001) higher mean daily coumarin dose than CC homozygotes to reach a stable international normalized ratio (INR). There was no evidence of publication bias. Heterogeneity among studies was present (I(2) = 43%). Our results show that the CYP4F2 p.V433M polymorphism is associated with interindividual variability in response to coumarin drugs, but with a low effect size that is confirmed to be lower than those contributed by VKORC1 and CYP2C9 polymorphisms.
Conflict of interest statement
J.A.J. is a member of the Clarification of Optimal Anticoagulation Through Genetics (COAG) clinical trial executive committee. S.A.S.,T.L, and J.F.C. are members of the COAG genotyping committee. The other authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
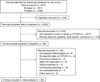

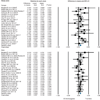
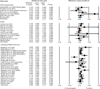

References
-
- Ansell J, Hirsh J, Poller L, Bussey H, Jacobson A, Hylek E. The pharmacology and management of the vitamin K antagonists: the Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. Chest. 2004;126:204S–233S. - PubMed
-
- Budnitz DS, Lovegrove MC, Shehab N, Richards CL. Emergency hospitalizations for adverse drug events in older Americans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011;365:2002–2012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

