Foamy virus envelope protein is a substrate for signal peptide peptidase-like 3 (SPPL3)
- PMID: 23132852
- PMCID: PMC3527927
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.371369
Foamy virus envelope protein is a substrate for signal peptide peptidase-like 3 (SPPL3)
Abstract
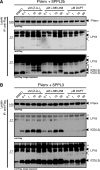
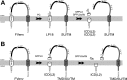
Signal peptide peptidase (SPP), its homologs, the SPP-like proteases SPPL2a/b/c and SPPL3, as well as presenilin, the catalytic subunit of the γ-secretase complex, are intramembrane-cleaving aspartyl proteases of the GxGD type. In this study, we identified the 18-kDa leader peptide (LP18) of the foamy virus envelope protein (FVenv) as a new substrate for intramembrane proteolysis by human SPPL3 and SPPL2a/b. In contrast to SPPL2a/b and γ-secretase, which require substrates with an ectodomain shorter than 60 amino acids for efficient intramembrane proteolysis, SPPL3 cleaves mutant FVenv lacking the proprotein convertase cleavage site necessary for the prior shedding. Moreover, the cleavage product of FVenv generated by SPPL3 serves as a new substrate for consecutive intramembrane cleavage by SPPL2a/b. Thus, human SPPL3 is the first GxGD-type aspartyl protease shown to be capable of acting like a sheddase, similar to members of the rhomboid family, which belong to the class of intramembrane-cleaving serine proteases.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

