Transmembrane topology and oligomeric structure of the high-affinity choline transporter
- PMID: 23132865
- PMCID: PMC3522279
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.405027
Transmembrane topology and oligomeric structure of the high-affinity choline transporter
Abstract
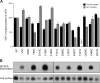
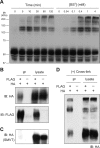
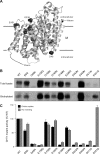
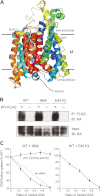
The high-affinity choline transporter CHT1 mediates choline uptake essential for acetylcholine synthesis in cholinergic nerve terminals. CHT1 belongs to the Na(+)/glucose cotransporter family (SLC5), which is postulated to have a common 13-transmembrane domain core; however, no direct experimental evidence for CHT1 transmembrane topology has yet been reported. We examined the transmembrane topology of human CHT1 using cysteine-scanning analysis. Single cysteine residues were introduced into the putative extra- and intracellular loops and probed for external accessibility for labeling with a membrane-impermeable, sulfhydryl-specific biotinylating reagent in intact cells expressing these mutants. The results provide experimental evidence for a topological model of a 13-transmembrane domain protein with an extracellular amino terminus and an intracellular carboxyl terminus. We also constructed a three-dimensional homology model of CHT1 based on the crystal structure of the bacterial Na(+)/galactose cotransporter, which supports our conclusion of CHT1 transmembrane topology. Furthermore, we examined whether CHT1 exists as a monomer or oligomer. Chemical cross-linking induces the formation of a higher molecular weight form of CHT1 on the cell surface in HEK293 cells. Two different epitope-tagged CHT1 proteins expressed in the same cells can be co-immunoprecipitated. Moreover, co-expression of an inactive mutant I89A with the wild type induces a dominant-negative effect on the overall choline uptake activity. These results indicate that CHT1 forms a homo-oligomer on the cell surface in cultured cells.
Figures


References
-
- Okuda T., Haga T. (2003) High-affinity choline transporter. Neurochem. Res. 28, 483–488 - PubMed
-
- Ferguson S. M., Blakely R. D. (2004) The choline transporter resurfaces. New roles for synaptic vesicles? Mol. Interv. 4, 22–37 - PubMed
-
- Sarter M., Parikh V. (2005) Choline transporters, cholinergic transmission and cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6, 48–56 - PubMed
-
- Ribeiro F. M., Black S. A., Prado V. F., Rylett R. J., Ferguson S. S., Prado M. A. (2006) The “ins” and “outs” of the high-affinity choline transporter CHT1. J. Neurochem. 97, 1–12 - PubMed
-
- Ribeiro F. M., Alves-Silva J., Volknandt W., Martins-Silva C., Mahmud H., Wilhelm A., Gomez M. V., Rylett R. J., Ferguson S. S., Prado V. F., Prado M. A. (2003) The hemicholinium-3 sensitive high affinity choline transporter is internalized by clathrin-mediated endocytosis and is present in endosomes and synaptic vesicles. J. Neurochem. 87, 136–146 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

