Genome-scale coestimation of species and gene trees
- PMID: 23132911
- PMCID: PMC3561873
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.141978.112
Genome-scale coestimation of species and gene trees
Abstract
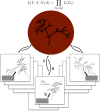
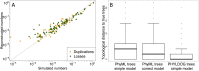
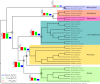
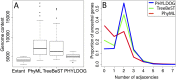
Comparisons of gene trees and species trees are key to understanding major processes of genome evolution such as gene duplication and loss. Because current methods to reconstruct phylogenies fail to model the two-way dependency between gene trees and the species tree, they often misrepresent gene and species histories. We present a new probabilistic model to jointly infer rooted species and gene trees for dozens of genomes and thousands of gene families. We use simulations to show that this method accurately infers the species tree and gene trees, is robust to misspecification of the models of sequence and gene family evolution, and provides a precise historic record of gene duplications and losses throughout genome evolution. We simultaneously reconstruct the history of mammalian species and their genes based on 36 completely sequenced genomes, and use the reconstructed gene trees to infer the gene content and organization of ancestral mammalian genomes. We show that our method yields a more accurate picture of ancestral genomes than the trees available in the authoritative database Ensembl.
Figures

References
-
- Arvestad L 2003. Bayesian gene/species tree reconciliation and orthology analysis using MCMC. Bioinformatics 19: i7–i15 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
