STING manifests self DNA-dependent inflammatory disease
- PMID: 23132945
- PMCID: PMC3511090
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1215006109
STING manifests self DNA-dependent inflammatory disease
Abstract
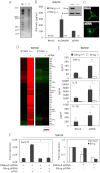
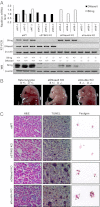
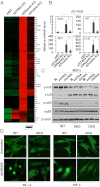
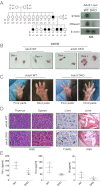
Inflammatory autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and polyarthritis are characterized by chronic cytokine overproduction, suggesting that the stimulation of host innate immune responses, speculatively by persistent infection or self nucleic acids, plays a role in the manifestation of these disorders. Mice lacking DNase II die during embryonic development through comparable inflammatory disease because phagocytosed DNA from apoptotic cells cannot be adequately digested and intracellular host DNA sensor pathways are engaged, resulting in the production of a variety of cytokines including type I IFN. The cellular sensor pathway(s) responsible for triggering DNA-mediated inflammation aggravated autoimmune disease remains to be determined. However, we report here that Stimulator of IFN Genes (STING) is responsible for inflammation-related embryonic death in DNase II defective mice initiated by self DNA. DNase II-dependent embryonic lethality was rescued by loss of STING function, and polyarthritis completely prevented because cytosolic DNA failed to robustly trigger cytokine production through STING-controlled signaling pathways. Our data provides significant molecular insight into the causes of DNA-mediated inflammatory disorders and affords a target that could plausibly be therapeutically controlled to help prevent such diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nagata S. Apoptosis and autoimmune diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1209:10–16. - PubMed
-
- Helmick CG, et al. National Arthritis Data Workgroup Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. Part I. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(1):15–25. - PubMed
-
- Crow MK. Type I interferon in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007;316:359–386. - PubMed
-
- Kawane K, et al. Requirement of DNase II for definitive erythropoiesis in the mouse fetal liver. Science. 2001;292(5521):1546–1549. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida H, Okabe Y, Kawane K, Fukuyama H, Nagata S. Lethal anemia caused by interferon-beta produced in mouse embryos carrying undigested DNA. Nat Immunol. 2005;6(1):49–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

