Deciphering the acylation pattern of Yersinia enterocolitica lipid A
- PMID: 23133372
- PMCID: PMC3486919
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002978
Deciphering the acylation pattern of Yersinia enterocolitica lipid A
Abstract
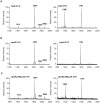
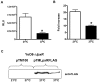
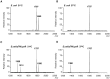
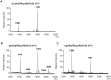
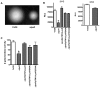
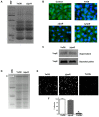
Pathogenic bacteria may modify their surface to evade the host innate immune response. Yersinia enterocolitica modulates its lipopolysaccharide (LPS) lipid A structure, and the key regulatory signal is temperature. At 21°C, lipid A is hexa-acylated and may be modified with aminoarabinose or palmitate. At 37°C, Y. enterocolitica expresses a tetra-acylated lipid A consistent with the 3'-O-deacylation of the molecule. In this work, by combining genetic and mass spectrometric analysis, we establish that Y. enterocolitica encodes a lipid A deacylase, LpxR, responsible for the lipid A structure observed at 37°C. Western blot analyses indicate that LpxR exhibits latency at 21°C, deacylation of lipid A is not observed despite the expression of LpxR in the membrane. Aminoarabinose-modified lipid A is involved in the latency. 3-D modelling, docking and site-directed mutagenesis experiments showed that LpxR D31 reduces the active site cavity volume so that aminoarabinose containing Kdo(2)-lipid A cannot be accommodated and, therefore, not deacylated. Our data revealed that the expression of lpxR is negatively controlled by RovA and PhoPQ which are necessary for the lipid A modification with aminoarabinose. Next, we investigated the role of lipid A structural plasticity conferred by LpxR on the expression/function of Y. enterocolitica virulence factors. We present evidence that motility and invasion of eukaryotic cells were reduced in the lpxR mutant grown at 21°C. Mechanistically, our data revealed that the expressions of flhDC and rovA, regulators controlling the flagellar regulon and invasin respectively, were down-regulated in the mutant. In contrast, the levels of the virulence plasmid (pYV)-encoded virulence factors Yops and YadA were not affected in the lpxR mutant. Finally, we establish that the low inflammatory response associated to Y. enterocolitica infections is the sum of the anti-inflammatory action exerted by pYV-encoded YopP and the reduced activation of the LPS receptor by a LpxR-dependent deacylated LPS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


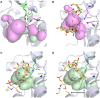


Similar articles
-
Role of lipid A acylation in Yersinia enterocolitica virulence.Infect Immun. 2010 Jun;78(6):2768-81. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01417-09. Epub 2010 Apr 12. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20385763 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of Yersinia enterocolitica temperature-dependent resistance to antimicrobial peptides.J Bacteriol. 2012 Jun;194(12):3173-88. doi: 10.1128/JB.00308-12. Epub 2012 Apr 13. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22505678 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between Yersinia enterocolitica and the host with special reference to virulence plasmid encoded adhesion and humoral immunity.Dan Med Bull. 1992 Apr;39(2):155-72. Dan Med Bull. 1992. PMID: 1611921 Review.
-
Release of the lipopolysaccharide deacylase PagL from latency compensates for a lack of lipopolysaccharide aminoarabinose modification-dependent resistance to the antimicrobial peptide polymyxin B in Salmonella enterica.J Bacteriol. 2007 Jul;189(13):4911-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.00451-07. Epub 2007 May 4. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17483225 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial cell surface structures in Yersinia enterocolitica.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2012 Jun;60(3):199-209. doi: 10.1007/s00005-012-0168-z. Epub 2012 Apr 8. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2012. PMID: 22484801 Review.
Cited by
-
Kdo2 -lipid A: structural diversity and impact on immunopharmacology.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2015 May;90(2):408-27. doi: 10.1111/brv.12114. Epub 2014 May 16. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2015. PMID: 24838025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Genomic Screen Identifies Klebsiella pneumoniae Factors Implicated in Blocking Nuclear Factor κB (NF-κB) Signaling.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jul 3;290(27):16678-97. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.621292. Epub 2015 May 13. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25971969 Free PMC article.
-
Leptospira interrogans lpxD Homologue Is Required for Thermal Acclimatization and Virulence.Infect Immun. 2015 Nov;83(11):4314-21. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00897-15. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26283339 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid A heterogeneity and its role in the host interactions with pathogenic and commensal bacteria.Microlife. 2022 Jun 10;3:uqac011. doi: 10.1093/femsml/uqac011. eCollection 2022. Microlife. 2022. PMID: 37223360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fortifying the barrier: the impact of lipid A remodelling on bacterial pathogenesis.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013 Jul;11(7):467-81. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3047. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23748343 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van HC, et al. (1998) Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 282: 2085–2088. - PubMed
-
- Trent MS, Stead CM, Tran AX, Hankins JV (2006) Diversity of endotoxin and its impact on pathogenesis. J Endotoxin Res 12: 205–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

