Effects of Puerariae Radix Extract on Endotoxin Receptors and TNF-α Expression Induced by Gut-Derived Endotoxin in Chronic Alcoholic Liver Injury
- PMID: 23133491
- PMCID: PMC3485520
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/234987
Effects of Puerariae Radix Extract on Endotoxin Receptors and TNF-α Expression Induced by Gut-Derived Endotoxin in Chronic Alcoholic Liver Injury
Abstract
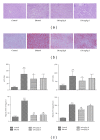
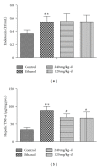
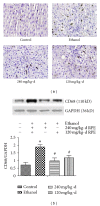
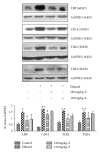
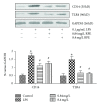
Kudzu (Pueraria lobata) is one of the earliest medicinal plants used to treat alcohol abuse in traditional Chinese medicine for more than a millennium. However, little is known about its effects on chronic alcoholic liver injury. Therefore, the present study observed the effects of puerariae radix extract (RPE) on chronic alcoholic liver injury as well as Kupffer cells (KCs) activation to release tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) induced by gut-derived endotoxin in rats and macrophage cell line. RPE was observed to alleviate the pathological changes and lipids deposition in liver tissues as well as the serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and hepatic gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) activity. Meanwhile, RPE inhibited KCs activation and subsequent hepatic TNF-α expression and downregulated the protein expression of endotoxin receptors, lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP), CD14, Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2, and TLR4 in chronic alcohol intake rats. Furthermore, an in vitro study showed that RPE inhibited the expression of TNF-α and endotoxin receptors, CD14 and TLR4, induced by LPS in RAW264.7 cells. In summary, this study demonstrated that RPE mitigated liver damage and lipid deposition induced by chronic alcohol intake in rats, as well as TNF-α release, protein expression of endotoxin receptors in vivo or in vitro.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Puerarin ameliorates experimental alcoholic liver injury by inhibition of endotoxin gut leakage, Kupffer cell activation, and endotoxin receptors expression.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013 Mar;344(3):646-54. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.201137. Epub 2012 Dec 31. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013. PMID: 23277536
-
[Relationship between alcoholic liver injury and endotoxin leakage from gut and intervention effect of jianpi liqi huoxue decoction].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2006 Sep;26(9):813-7. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17058832 Chinese.
-
Effects of traditional chinese medicine on endotoxin and its receptors in rats with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.Inflammation. 2008 Apr;31(2):121-32. doi: 10.1007/s10753-008-9057-3. Epub 2008 Feb 27. Inflammation. 2008. PMID: 18302012
-
[Ethanol changes sensitivity of Kupffer cells to endotoxin].Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi. 2003 Oct;38(5):415-24. Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 14639920 Review. Japanese.
-
Common pathogenic mechanism in development progression of liver injury caused by non-alcoholic or alcoholic steatohepatitis.J Toxicol Sci. 2007 Dec;32(5):453-68. doi: 10.2131/jts.32.453. J Toxicol Sci. 2007. PMID: 18198478 Review.
Cited by
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α, a potential therapeutic target for alcoholic liver disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul 7;20(25):8055-60. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8055. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25009377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lysimachiae Herba Inhibits Inflammatory Reactions and Improves Lipopolysaccharide/D-Galactosamine-Induced Hepatic Injury.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Aug 30;10(9):1387. doi: 10.3390/antiox10091387. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573019 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of autophagy attenuates EtOH-LPS-induced hepatic steatosis and injury through MD2 associated TLR4 signaling.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 24;7(1):9292. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09045-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28839246 Free PMC article.
-
Achyrocline satureioides (Lam.) D.C. Hydroalcoholic Extract Inhibits Neutrophil Functions Related to Innate Host Defense.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:787916. doi: 10.1155/2013/787916. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23476704 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of the gut-liver axis in the pathogenesis of acute-on-chronic liver failure.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Feb;30(2):130-135. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001026. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29200007 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- O’Shea RS, Dasarathy S, McCullough AJ. Alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 2010;51(307):p. 328. - PubMed
-
- Lu X, Tao M, Luo J, Geng Y, Zhao H, Zhao P. Epidemiology of alcohol and liver disease. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2002;10(6):467–468. - PubMed
-
- Bykov I, Järveläinen H, Lindros K. L-carnitine alleviates alcohol-induced liver damage in rats: role of tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Alcohol and Alcoholism. 2003;38(5):400–406. - PubMed
-
- Fischer M, You M, Matsumoto M, Crabb DW. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) agonist treatment reverses PPARα dysfunction and abnormalities in hepatic lipid metabolism in ethanol-fed mice. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2003;278(30):27997–28004. - PubMed
-
- Galli A, Pinaire J, Fischer M, Dorris R, Crabb DW. The transcriptional and DNA binding activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α is inhibited by ethanol metabolism. A novel mechanism for the development of ethanol-induced fatty liver. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2001;276(1):68–75. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

